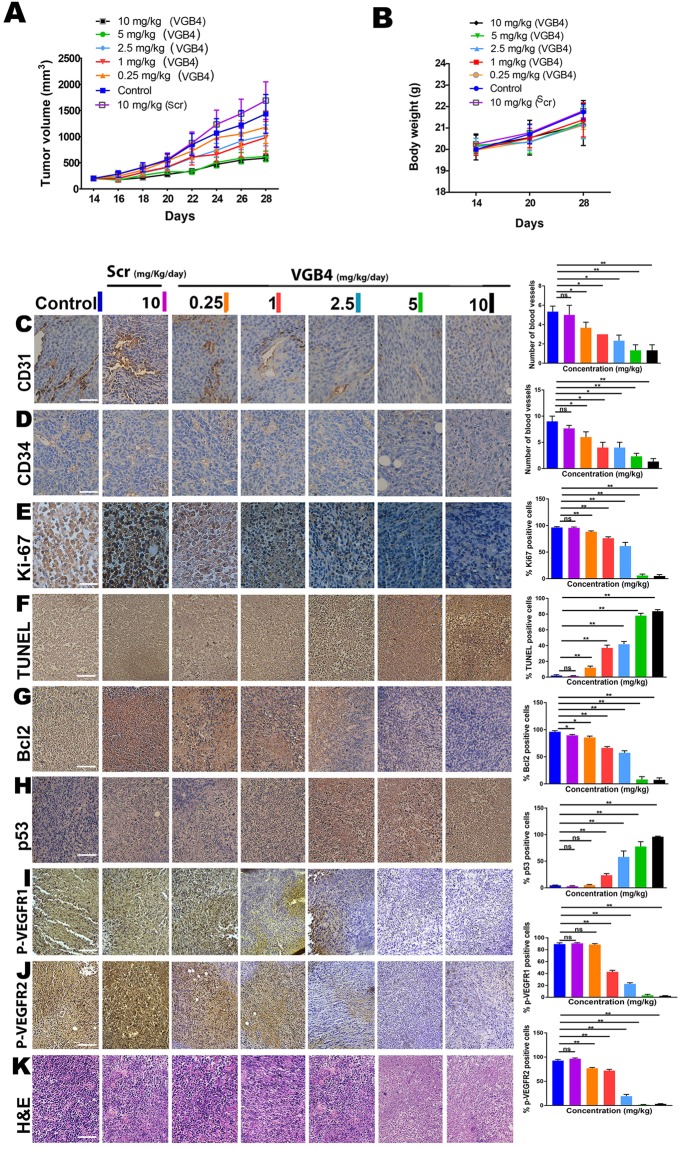
Figure 6.
The inhibitory effect of VGB4 on tumor growth, metastasis and signaling pathways in vivo. (A) 4T1 murine MCT was transplanted into female BALB/c mice. On day 14 after transplantation (when the tumor volume reached ~200 mm3), animals in the experimental groups were treated daily with intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection of different doses (0.25, 1, 2.5, 5 and 10 mg/kg/day) of VGB4 or (10 mg/kg) scr, whereas control mice received equal volume of PBS (n = 7 mice for each group). (B) The average body weight of each group was measured on days 14, 20 and 28 then expressed as the mean ± SD (n = 7 per group). (C–K) Immunohistochemical analyses. Representative images and quantitative analysis of (C) CD31, (D) CD34, (E) Ki-67 staining (Magnification 40×; bar = 20 µm) and (F) TUNEL, (G) Bcl2, (H) P53, (I) p-VEGFR1, (J) p-VEGFR2 and (K) H&E staining (Magnification 10×; bar = 100 µm) of VGB4 treated tumors and PBS-treated tumors 28 days after subcutaneous transplantation of 4T1 MCTs in BALB/c mice. All data were represented as mean ± SD, n = 3, *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.001, compared to the control group.