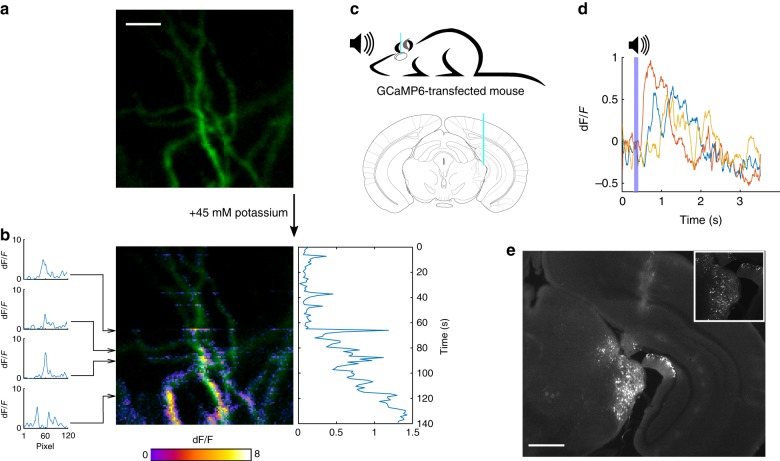
Fig. 4. The MMF-based system captures dynamic changes in neuronal Ca2+ signals.
a A neuron in a rat organotypic hippocampal slice was filled with the Ca2 + -sensitive dye OGB-1. b After bath application of 45 mM potassium, a gradual increase in intracellular Ca2+ resulting from the depolarization of the neuron was detected through dynamic changes in fluorescence. The traces on the left show the variation in florescence during the scanning of individual lines of the image, each 120 pixels. The trace on the right is the average dF/F for all scanned lines and shows the gradual increase in intracellular Ca2+ from the moment in which potassium is added to the bath. Scale bar: 10 μm. c An MMF was lowered 3 mm into the MGB of an anesthetized mouse presented with auditive stimuli (top). Atlas depiction indicating the placement of the MMF (blue); adapted from the Allen Mouse Brain Atlas (bottom). d Calcium responses recorded from a single pixel were elicited by repeated presentation of a 100-ms pure tone of 16 kHz (purple bar). Color traces show the responses from individual trials. e Post-mortem histological analysis showed sparse expression of the genetically encoded calcium indicator GCaMP6m in the MGB and fiber track. The inset shows the MGB neuron labeling. Scale bar: 1 mm