Figure 2.
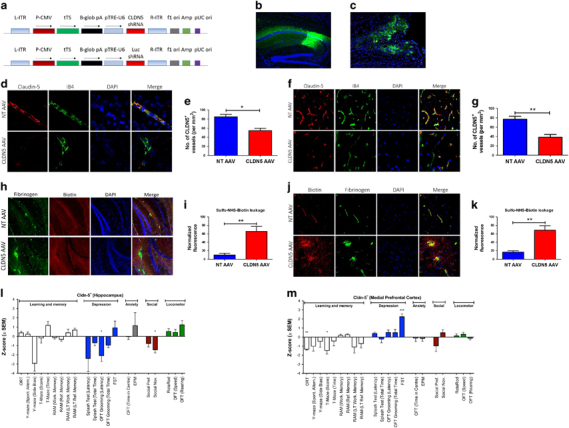
Site-specific suppression of claudin-5 in the hippocampus and medial prefrontal cortex. (a) Plasmid maps of claudin-5 AAV-2/9 and non-targeting (NT) AAV-2/9. (b) eGFP-expressing AAV-2/9 injected into the dorsal hippocampus. (c) eGFP-expressing AAV-2/9 injected into the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC). (d and e) Significant suppression of claudin-5 (red) in the microvasculature of the hippocampus (IB4: green, DAPI: blue; scale bar: 50 μm; *P<0.05). (f and g) Significant suppression of claudin-5 (red) in the microvasculature of the mPFC (IB4: green, DAPI: blue; scale bar: 50 μm; **P<0.01). (h) Biotin (red) and fibrinogen (green) extravasation in the hippocampus; scale bar: 50 μm. (i) Quantification of biotin extravasation in the hippocampus, suppression of claudin-5 significantly increases the amount of extravasation (**P<0.01). (j) Biotin (red) and fibrinogen (green) extravasation in the mPFC; scale bar: 50 μm. (k) Quantification of biotin extravasation in the mPFC, suppression of claudin-5 significantly increases the amount of biotin extravasation (**P<0.01). (l) Summary of behavioural data following suppression of claudin-5 in the hippocampus. These mice showed significantly decreased levels of grooming (*P<0.05) along with a significant impairment in the social novelty task (*P<0.05). (m) Summary of behavioural data following suppression of claudin-5 in the mPFC. These mice showed significant impairments in the social object recognition task (**P<0.01) and the T-maze (*P<0.05) along with a significant enhancement in the forced swim test (***P<0.001). Behavioural assays were performed 2 weeks post supplementation of doxycycline (2 mg/ml) to the drinking water. AAV, adeno-associated virus; eGFP, enhanced green fluorescent protein; EPM, elevated plus maze; FST, forced swimming test; LT, long-term; shRNA, short hairpin RNA; RAM, radial arm maze; OFT, open field test.
