Figure 3.
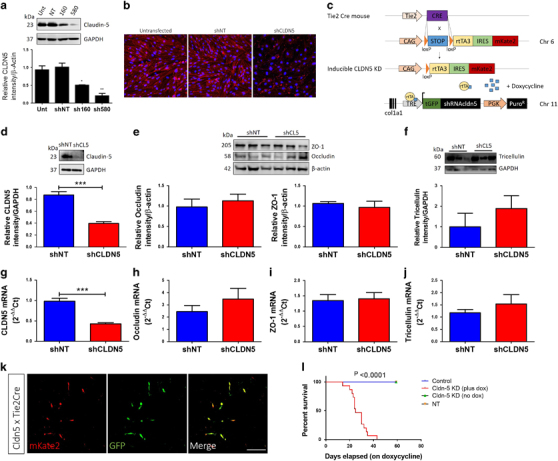
Generation and characterization of inducible claudin-5 knockdown mice. (a) Significant suppression of claudin-5 expression 24 h post transfection of two different shRNAs targeting claudin-5 in vitro (*P<0.05; **P<0.01). (b) Levels of expression of claudin-5 at the tight junction 24 h post transfection of claudin-5 shRNA in a monolayer of mouse brain endothelial cells; scale bar: 50 μm. (c) Schematic representation of inducible claudin-5 knockdown mouse model. (d) Inducible suppression of claudin-5 protein using shRNA in the vasculature of the mouse brain (***P<0.001) 72 h following i.p. injection of 40 mg/kg doxycycline in 0.9% saline. No significant changes in the protein expression levels of the other tight junction proteins, (e) occludin, and ZO-1 and (f) tricellulin. (g) Inducible suppression of claudin-5 mRNA using shRNA in the vasculature of the mouse brain (***P<0.001). No changes in the transcript levels of (h) occludin, (i) ZO-1 or (j) tricellulin. (k) Expression of rtTA3 (red, mKate) and claudin-5 shRNA (green, turbo green fluorescent protein) confirmed in the vasculature of the mouse brain 72 h following i.p. injection of doxycycline; scale bar: 50 μm. (l) Survival chart for inducible claudin-5 knockdown mice. Inducible claudin-5 knockdown mice supplemented with doxycycline (2 mg/ml) all die compared to inducible claudin-5 mice fed water only, a scrambled control mouse (NT) and Cre-negative littermates. mRNA, messenger RNA; NT, non-targeting; shRNA, short hairpin RNA.
