Figure 4.
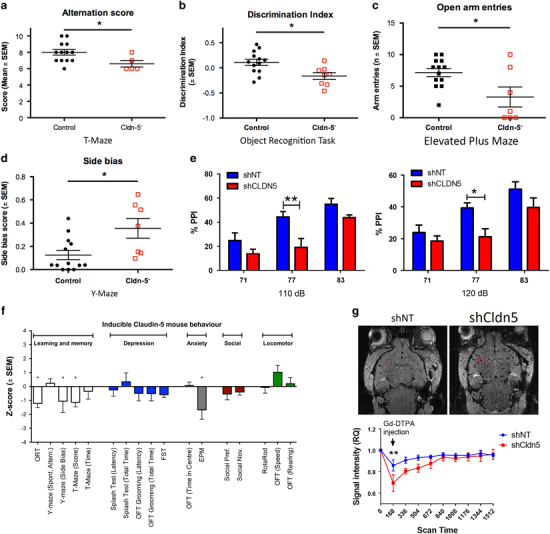
Phenotype of inducible claudin-5 knockdown mice. (a) Reduced spontaneous alternation in the T-maze in claudin-5 knockdown mice (*P<0.05). (b) Reduced discrimination index in claudin-5 knockdown mice in the object recognition task (*P<0.05). (c) Reduced open arm entries observed in the elevated plus maze in the claudin-5 knockdown mice (*P<0.05). (d) Increased side bias in inducible claudin-5 knockdown mice in a spontaneous alternation task in the Y-maze (*P<0.05). (e) Decreased acoustic prepulse inhibition (PPI) in inducible claudin-5 knockdown mice with a 77 dB prepulse at 110 dB (**P<0.01) and 120 dB (*P<0.05). (f) Summary of behavioural data following suppression of claudin-5 in the inducible claudin-5 knockdown mouse model. (g) Contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showing significant extravasation of contrast agent in the brain of inducible claudin-5 knockdown mice (right) compared to non-targeting control mice (left; **P<0.01). All assays were performed 2–4 weeks post supplementation of doxycycline (2 mg/ml) to the drinking water. RQ, relative quantity.
