Figure 5.
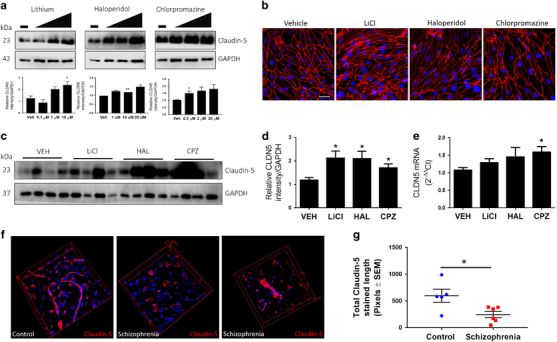
Regulation of claudin-5 levels by anti-psychotic drugs and examples of aberrant claudin-5 expression in schizophrenia. (a) Levels of expression of claudin-5 in primary mouse brain endothelial cells exposed for 24 h to lithium (LiCl), haloperidol (HAL) or chlorpromazine (CPZ). (b) Immunocytochemical analysis of claudin-5 (red)-staining pattern in primary mouse brain endothelial cells treated with anti-psychotic drugs; scale bar: 50 μm. (c) Levels of expression of claudin-5 in capillary fractions from mouse brains 24 h following administration (i.v.) of LiCl, HAL or CPZ. (d) Claudin-5 expression was significantly higher in mice treated with antipsychotics (*P<0.05). (e) Claudin-5 mRNA levels were significantly higher in mice treated with CPZ (*P<0.05). (f) Claudin-5 levels in normal control or schizophrenia donor brain tissues from the parietal lobe. Sixty-two per cent of schizophrenia patients showed aberrant claudin-5 staining in the parietal lobe. (g) There are significantly lower levels of claudin-5 in the parietal lobe in individuals who have a diagnosis of schizophrenia and the presence of the rs10314 allele compared to controls who have the rs10314 allele (*P<0.05).
