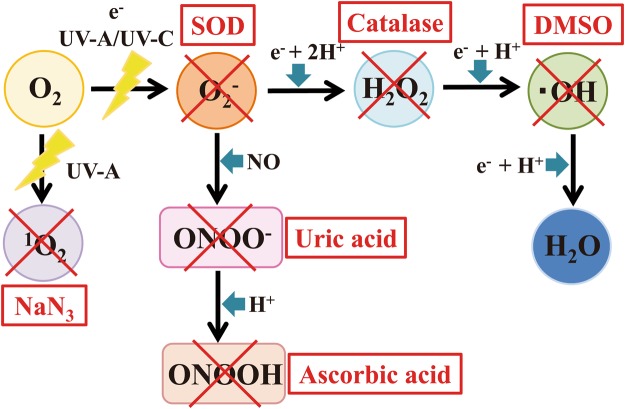
Figure 7.
Radical scavengers and reactions. After exposure to UV-A, O2 is converted into 1O2. The 1O2 is eliminated by sodium azide (NaN3), which acts as a scavenger. After exposure to UV-A/UV-C or electrons (e−), O2 is converted into the superoxide anion radical (·O2−), which is eliminated by superoxide dismutase (SOD). ·O2− is converted into H2O2 after reaction with e− + 2H+. H2O2 is eliminated by catalase. After the reaction with e− + H+, H2O2 is converted into a hydroxyl radical (·OH). ·OH is eliminated by dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). After the reaction with e− + H+, ·OH is converted into H2O. After the reaction with NO, O2− is converted into ONOO−, which is eliminated by uric acid. ONOO− is then converted into ONOOH after reaction with H+, and ONOOH is eliminated by ascorbic acid.