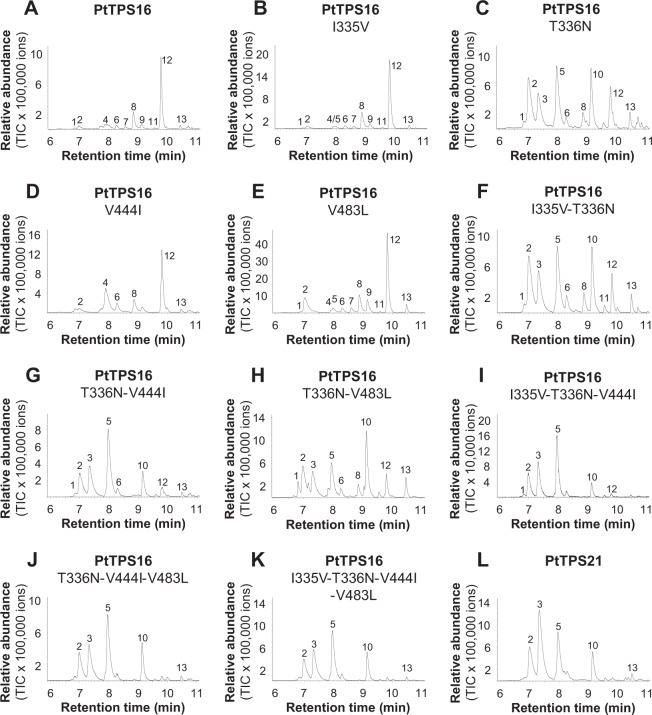
Figure 5.
Biochemical characterization of PtTPS16 mutants generated using in vitro mutagenesis. GC-MS chromatograms representing the product spectra of wild type PtTPS16 (A), wild type PtTPS21 (L), and the different PtTPS16 mutants (B–K) are shown. Amino acid changes (one letter code) and their positions relative to the PtTPS16 sequence are indicated in the name of the mutants. The genes were heterologously expressed in E. coli and partially purified proteins were incubated with GPP as substrate. Enzyme products were analyzed using GC-MS. 1, α-thujene; 2, α-pinene*; 3, camphene*; 4, sabinene; 5, β-pinene*; 6, myrcene; 7, α-phellandrene; 8, α-terpinene*; 9, β-phellandrene; 10, limonene*; 11, ocimene; 12, γ-terpinene*; 13, terpinolene. Compounds marked with * were identified by comparison of retention time and mass spectrum to those of authentic standards. Others were identified by database comparisons.