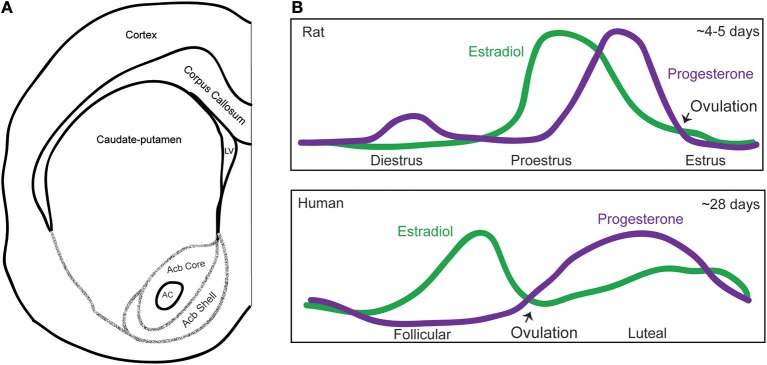
Figure 1.
Map of the striatal subregions and female hormone cycling. (A) Schematic of a coronal section of one hemisphere of the rat brain depicting the striatal subregions, including the caudate-putamen, nucleus accumbens core, and shell (Interaural ~10.92–10.80 mm, Bregma ~1.92–1.80 mm). Acronyms: AC, anterior commissure; Acb, nucleus accumbens; LV, lateral ventricle. The extensive afferent and efferent circuitry of the striatal subregions is not depicted in this schematic, and we refer the reader to the following articles for a review of this topic (Russo and Nestler, 2013; Scofield et al., 2016) (B) Graphical depictions of the adult female rat estrous and human menstrual cycle. Purple line indicates progesterone levels and the green line estradiol levels. Over a span of about 4–5 days, rats exhibit a diestrus, proestrus, and estrus phase. There is also a metestrus phase between estrus and diestrus (not pictured). In rats, estradiol levels peak the morning of proestrus, as progesterone levels are rising, and behavioral estrus begins roughly when progesterone levels peak. The human cycle lasts about 28 days, and exhibits a follicular and luteal phase. In humans, estradiol peaks during the follicular phase, and progesterone peaks during the luteal phase.