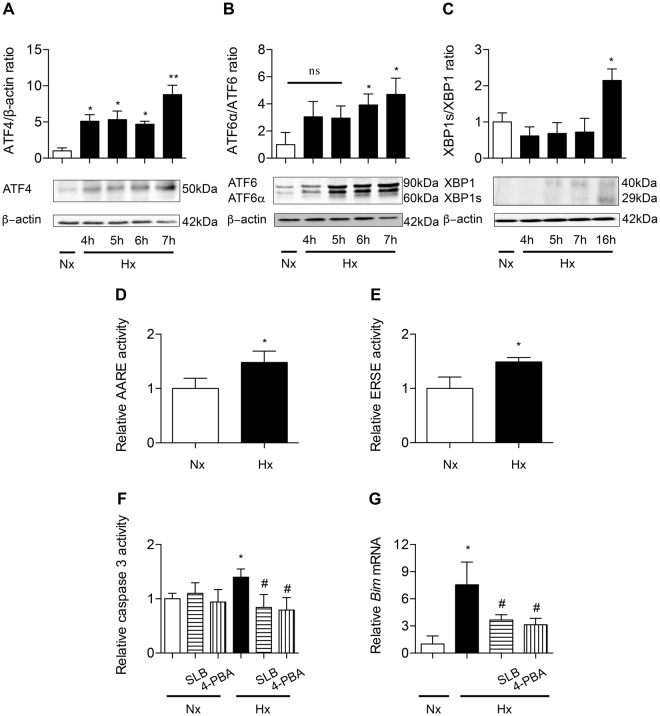
Figure 5.
ER stress is involved in hypoxia-induced alveolar epithelial cells apoptosis. Primary rat AECs were placed in normoxia (Nx) (21% of O2) or exposed to hypoxia (Hx) (1.5% of O2) for increasing times (4–24 h). Protein levels of ATF4 (A), ATF6α/ATF6 ratio (B) and XBP1s/XBP1 ratio (C) were evaluated by western blotting. Quantification has been done on at least 5 independent experiments, representing the densitometry analysis of each proteins of interest reported to β-actin. Primary rat AECs were transfected with plasmids coding for luciferase reporter activity of ATF4 (the amino acid response element: AARE) (D) or ATF6α/XBP1s (the endoplasmic reticulum response element: ERSE) (E) and exposed to hypoxia for 6 h. Primary rat AECs were placed in normoxia or exposed to hypoxia for 24 h in the presence or absence of ER stress modulators salubrinal (SLB, 100 µM) or 4-phenylbutyrate (4-PBA, 100 mM). The activity of effector caspase 3 was evaluated by enzymatic assay (F), and expression of the pro apoptotic marker Bim was evaluated by RT-qPCR (G). n = at least 5 independent experiments. Data were submitted to a Kruskal-Wallis one-way analysis of variance followed by a Dunn’s multiple comparison tests, except for AARE and ERSE activity data submitted to a Mann-Whitney analysis. *P < 0.05, and **P < 0.01: significantly different from control value in normoxic cells. #P < 0.05: significantly different from the value in untreated hypoxic cells. ns: non-significant difference between normoxic condition and hypoxic condition.