Fig. 3.
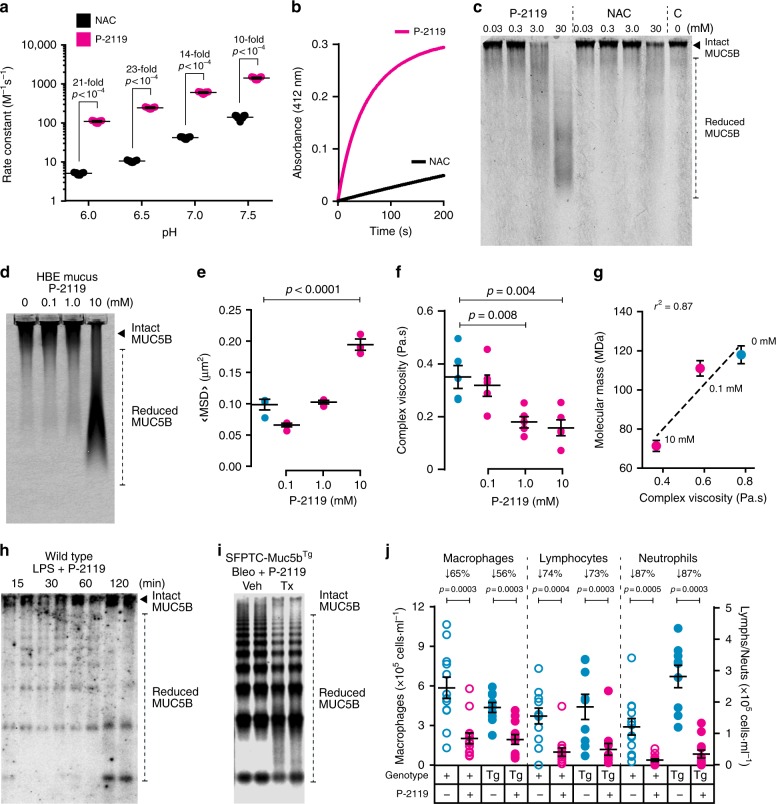
P-2119 effectively cleaves mucus in vitro and in vivo, enhancing the acute clearance of inflammatory cells. a, b P-2119 hydrolyzed DTNB disulfide bonds more quickly than n-acetylcysteine (NAC) a, and at pH 6 P-2119 cleaved more bonds than NAC b. c In human saliva, P-2119 reduced MUC5B in salivary mucus at lower concentrations than NAC. d–g In concentrated normal human bronchial epithelial cell culture mucus (5% solids), P-2119 reduced MUC5B at a potency similar to that seen in saliva in c. Reduction of MUC5B by P-2119 dose dependently lowered mucus viscosity as demonstrated by enhanced mean square displacement (MSD) of fluorescent microspheres e, and as shown by improved macrorheological complex viscosity f that was strongly correlated with reduced molecular mass g. Data in e represent 900 technical and three biological replicates; data in f represent three technical and two biological replicates. Cyan symbols, vehicle; magenta symbols, P-2119. h–j In vivo effects of aerosolized P-2119 (68–135 mM for 60 min). h Wild-type mice challenged with LPS (20 μg, IT) 48 h prior to P-2119 aerosol. P-2119 decreased Muc5b mass detected by immunoblot of lung lavage fluid over a 120 min period. i SFTPC-Muc5bTg mice were challenged with bleomycin (2.5 U/kg, IT) 7 d prior to P-2119 treatment (Tx). P-2119 caused Muc5b reduction detected by immunoblot 120 min post initiation of P-2119 aerosol. j The effect of P-2119-induced mucolysis on MCC was assessed by quantifying the acute elimination of leukocytes in lung lavage fluid obtained from bleomycin treated SFTPC-Muc5bTg mice (n = 9 vehicle and 12 P-2119 treated) and wild type (+) controls (n = 12 vehicle and 13 P-2119 treated). Total cells were significantly lower in P-2119 treated mice compared to vehicle treated animals, reflecting decreases in all leukocyte subtypes in bleomycin-injured lungs. Data in a, e–g, and j are means ± sem. Data in a were analyzed between P-2119 and NAC treated groups using t-tests. Data in e–g were analyzed statistically on biological replicates: ANOVA of results between 0 mM vehicle and 0.1–10 mM P-2119 treatment groups e, f and linear regression of complex viscosity vs mass g