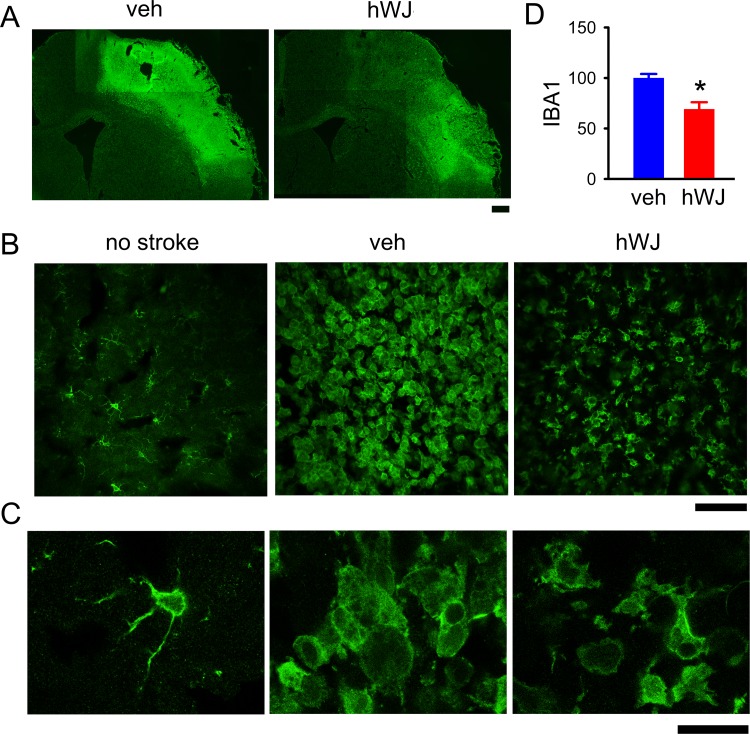
Fig 3.
Transplantation of hWJ-MSCs reduced the microglial activation in the peri-lesioned area. (A) IBA1 immunoreactivity was greatly increased in the peri-lesioned area of the ischemic cortex. (B) Transplantation of hWJ-MSCs reduced the IBA1 immunoreactivity in stroke brains (vehicle versus hWJ). (C) High-magnification images demonstrate de-ramified or amoeboid microglial cells in the peri-lesioned cortex in animals receiving vehicle, as compared with the resting microglia with ramified morphology in the non-lesioned side cortex. Ramified microglia were partially restored in the peri-lesioned area in animals receiving hWJ-MSCs. (D) The optical density of IBA1 immunoreactivity was quantified in the six different peri-lesioned areas in three consecutive brain sections with a visualized anterior commissure in each animal. Averaged IBA1 optical density in the peri-lesioned zone was significantly reduced by hWJ-MSCs transplantation. Calibration: (A) 1000 μm, (B) 50 μm, (C) 10 μm.
hWJ-MSC: Wharton’s jelly-derived mesenchymal stromal cell; IBA1: ionized calcium-binding adaptor molecule.