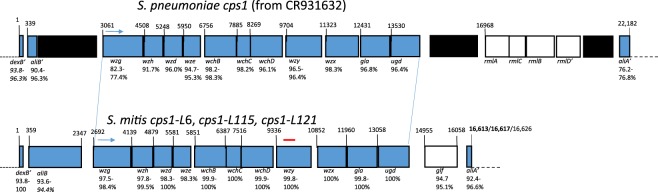
Figure 1.
Genomic sequencing results showing alignment of cps1 regions between serotype 1 S. pneumoniae and S. mitis. Comparison of cps1-L polysaccharide synthetic cluster regions from S. mitis strains L006/L164 (16,613 bp), L115/L116 (16,617 bp) and L121 (16,626 bp) with the corresponding pneumococcal cps1 sequence. White rectangles represent open reading frames not shared between the species. Top diagram depicts ranges of sequence identity between pneumococcal cps1 genes and the S. mitis counterparts depicted on the bottom diagram. Ranges of sequence identity between the S. mitis alleles are given below S. mitis cps1 diagram. L006 and L164 shared identical 16613 sequence. L115 and L116 shared identical 16617 bp sequence. The connecting blue lines depict the alignment of the polysaccharide synthesis clusters. Black regions in the pneumococcal diagram depict remnants of transposase genes. Two inactive pneumococcal genes (aliB and rmlD, the latter renders the rhamnose biosynthesis cluster inactive) containing frameshift mutations are indicated, as well as the partial 5′ and 3′ ends of the dexB and aliA genes in both species (′). The region detected through use of PCR assays to first detect the presence of these strains in upper respiratory specimens is depicted by the red line above the wzy gene.