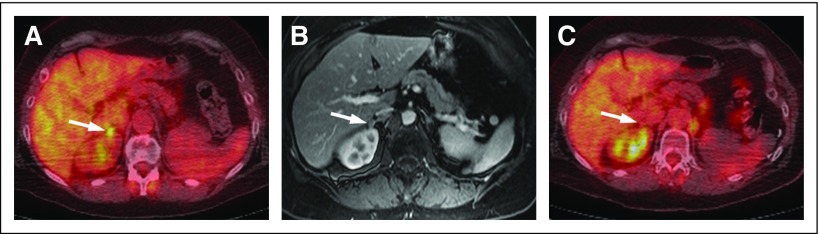
Fig A1.
Fifty-seven-year-old woman with metastatic renal cell carcinoma to the right adrenal gland. (A) Axial fused [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography/computed tomography image demonstrates a new (ie, compared with prior imaging [not shown]), small, FDG-avid right-side adrenal nodule (arrow) that represents a new site of oligometastatic disease. (B) Axial fat-suppressed T1-weighted contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance image confirms the presence of a small, right-sided adrenal nodule (arrow). (C) Follow-up axial fused FDG positron emission tomography/computed tomography image after microwave ablation demonstrates resolution of the focal-intense FDG uptake (arrow), which suggests adequate coverage of the lesion. No new sites of disease were present elsewhere.