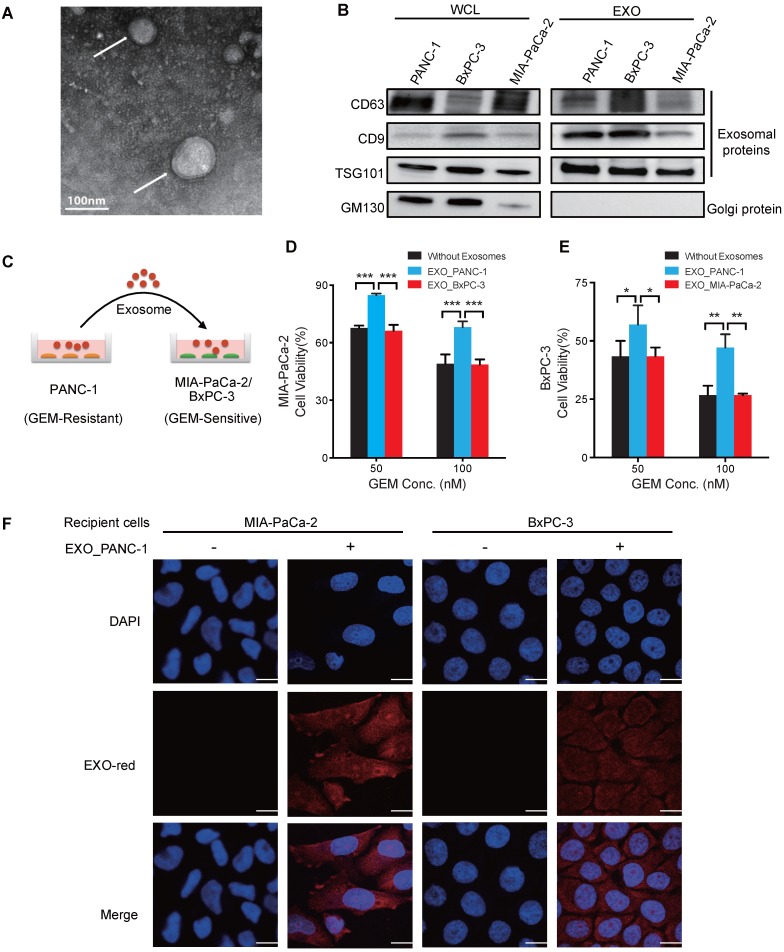
Figure 1.
Exosomes of GEM-resistant PC cells can transfer chemoresistance. (A) TEM image of exosomes isolated from PANC-1 cells and negatively stained by uranyl acetate (arrows). (B) Western blot analysis of exosomes (EXOs) and whole-cell lysates (WCLs) of PANC-1, MIA PaCa-2, and BxPC-3 cells for exosome (CD63, CD9, and TSG101) and golgi (GM130) protein markers. (C) Experimental design of exosome uptake studies. (D-E) GEM cytotoxicity in (D) MIA PaCa-2 cells or (E) BxPC-3 after 24 h pre-treatment with 20 µg/mL exosomes from PANC-1 (EXO_PANC-1), BxPC-3 (EXO_BxPC-3) or MIA PaCa-2 (EXO_MIA PaCa-2) cells, with fresh exosomes added every 24 h of the 3 day GEM treatment. Cell viability is presented as a percentage of control (no drug or exosomes) viability. (F) Exosome internalization in MIA PaCa-2 and BxPC-3 cells incubated for 2 h with or without EXO-Red-stained exosomes and then stained with DAPI for nuclear visualization. Bar indicates 10 µm; Data indicate mean±SD; n=6; *p<0.05; **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.