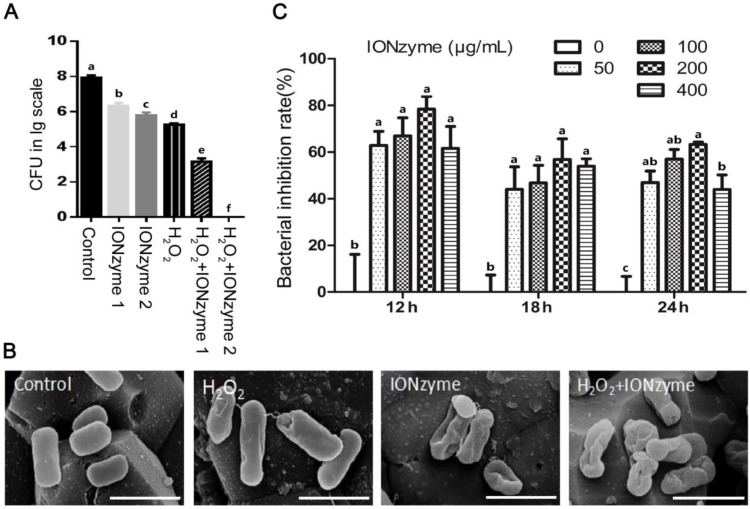
Figure 1.
The inhibition effects of IONzymes on S. Enteritidis. (A) The inhibition effects of IONzymes to planktonic S. Enteritidis in the absent or presence of H2O2. IONzyme 1: 0.25 mg/ml IONzyme; IONzyme 2: 0.5 mg/ml IONzyme; H2O2: 0.05% H2O2; H2O2+IONzyme 1: 0.05% H2O2+0.25 mg/ml IONzyme; H2O2+IONzyme 2: 0.05% H2O2+0.5 mg/ml IONzyme. (B) SEM micrographs of S. Enteritidis. S. Enteritidis were treated with vehicle control, H2O2 alone (0.05%), IONzymes alone (0.5 mg/mL), and the combination treatment of IONzymes (0.5 mg/mL) and H2O2 (0.05%). Scale bar: 10 µm. (C) The effect of dose- and time-response of IONzymes on S. Enteritidis infected-LMH cells. LMH cells were infected with 5×107 CFU/mL S. Enteritidis and treated with indicated concentrations of IONzymes (0, 50, 100, 200, and 400 μg/mL) to 12, 18 and 24 h. Bacterial inhibition rates were expressed as a percentage of the control group without IONzymes treatment. Data represented as Mean ± SEM (n=3). Different letters indicate statistically significant difference (P < 0.05).