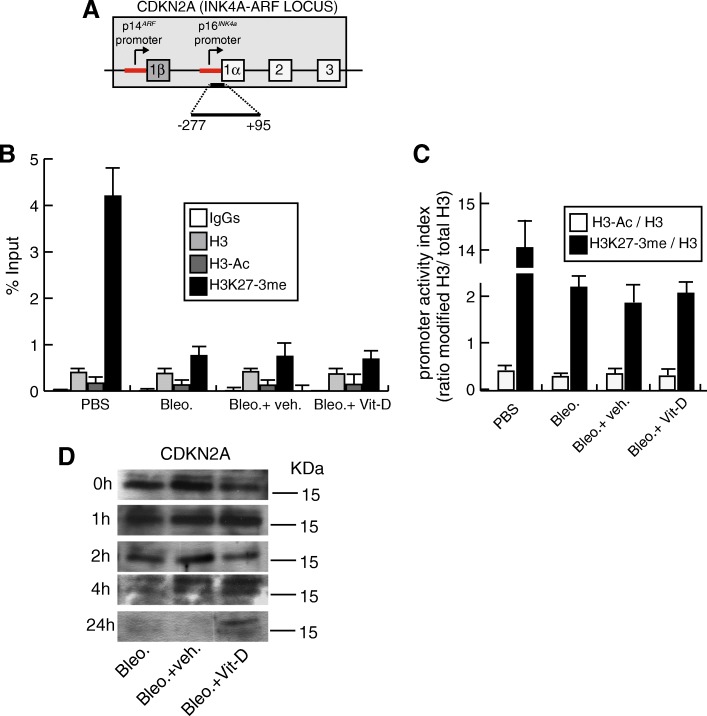
Fig. 6.
Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) analysis of the CDKN2A (p16INK4a) proximal promoter. a Diagram (not to scale) that illustrates the CDKN2A (INK4A-ARF) locus showing its exon/intron structure and the region analyzed corresponding to the proximal p16INK4a promoter (region − 277 to + 95). b ChIP result (% of input) obtained with normal IgGs, and the antibodies directed against histone H3 (H3), acetylated histone H3 (H3-Ac) and Histone H3 trimethylated in Lys27 (H3K27-3me). Cells were pretreated with vitamin D or its vehicle, subjected to a bleomycin shock (12 μg/mL for 6 h) and then treated with 5 nmol/L vitamin D or its vehicle. Control cultures correspond to cells treated with bleomycin vehicle (PBS). c Promoter activity index as determined by the ratio of the % input of modified histone H3/ % input of total histone H3. Transcriptional activation is determined by the ratio H3Ac/H3 and repression by the corresponding ratio H3K27-3me/H3. The results presented in the graphs are means ±SEM. ANOVA P < 0,0001. d Determination of CDKN2A protein half-life. Cells were pretreated with 5 nmol/L vitamin D or its vehicle, subjected to a bleomycin shock (12 μg/mL for 6 h) and then treated with 5 nmol/L of vitamin D or vehicle for 24 h. After that the cells were incubated with 100 μM of cycloheximide for 24 h. Detection of CDKN2A protein was performed in cell extracts of cultures released from cycloheximide inhibition at different times (from 0 to 24 h). KDa: kilodaltons