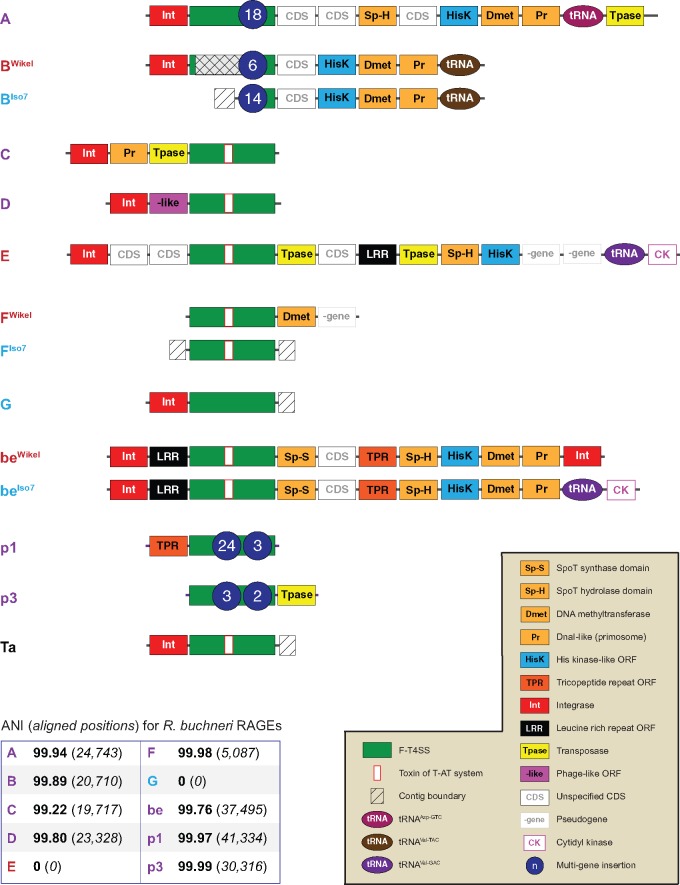
Fig. 2.
—Both sequenced isolates of Rickettsia buchneri contain multiple intact RAGE loci with evidence of genomic rearrangement. Gene order and functional annotations for each RAGE is shown in cartoon representation; see the included key (bottom right) for abbreviations and color scheme. RAGEs that are syntenic between isolates are labeled in purple. When two RAGEs differ between isolates, the R. buchneri str. Wikel variant is labeled in red and the R. buchneri str. ISO7 variant is labeled in blue. The novel RAGE-Ta described in this study is shown at the bottom and labeled in black. Gene order within the F-T4SS modules (green rectangles) and multigene insertions (blue ovals) are excluded for clarity; see supplementary tables S2 and S3, Supplementary Material online, for information on all the RAGE genes and their accession identifiers. Average nucleotide identities and the total aligned positions for shared RAGEs are shown in the grid at the bottom left; an ANI of 0% is listed for RAGEs that are unique to one isolate or the other.