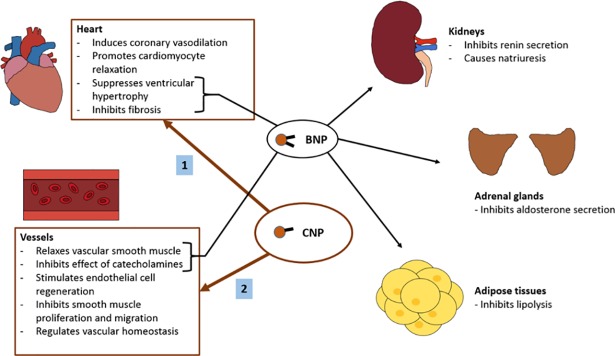
Fig 1. Function of C-type natriuretic peptide.
CNP is an endothelium-derived peptide that is believed to have a cardioprotective function in both healthy and disease states. While BNP directly causes natriuresis in addition to other functions, CNP acts primarily on the heart and blood vessels. In the heart, CNP induces coronary vasodilation, promotes cardiomyocyte relaxation, and exerts antihypertrophic and antifibrotic effects. In the vessels, CNP relaxes smooth muscle and inhibits its proliferation and migration, while also inhibiting catecholaminergic effects, stimulating endothelial cell regeneration, and regulating vascular homeostasis. (BNP–B-type natriuretic peptide, CNP–C-type natriuretic peptide).