Fig 5. Predicted inhibitors show direct binding to and functional inhibition of CHIP.
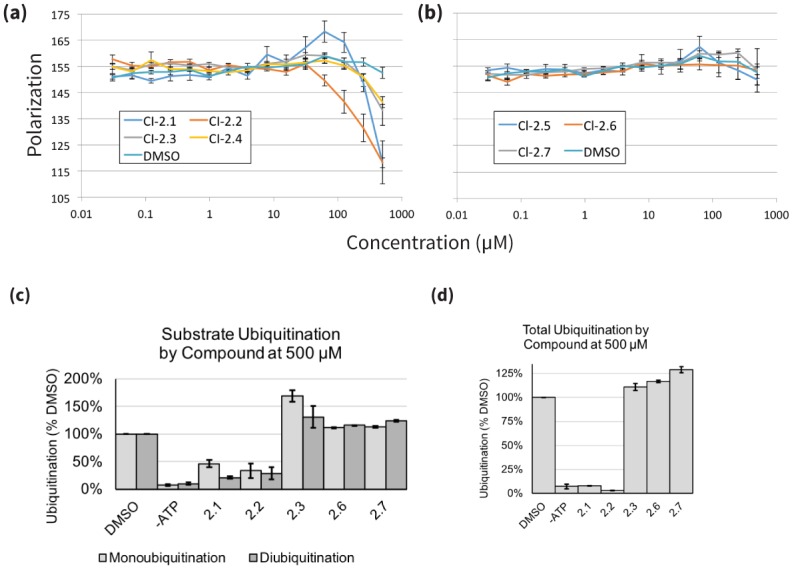
(a,b) Predicted CHIP inhibitors disrupt binding to chaperone peptide by fluorescence polarization. High ranked (a) and low ranked (b) compounds were tested for the ability to compete with a known TPR ligand (5-FAM-GSGPTIEEVD, 0.1 μM) for binding to CHIP (0.5 μM). Results are the average and standard error of the mean of two experiments each performed in triplicate. (c,d) CHIP inhibitors prevent ubiquitination by CHIP in vitro. (c) Quantification of substrate ubiquitination by CHIP from Anti-GST western blot experiments with tested compounds at 500 μM, blotted as in S5a Fig and normalized to DMSO treated control (2.1, 2.2: N = 4; all other compounds: N = 2). (d) Quantification of total ubiquitination by CHIP from Anti-GST western blot experiments with tested compounds at 500 μM, blotted as in S5b Fig and normalized to ubiquitination by a DMSO treated control (all compounds: N = 2).
