Figure 4.
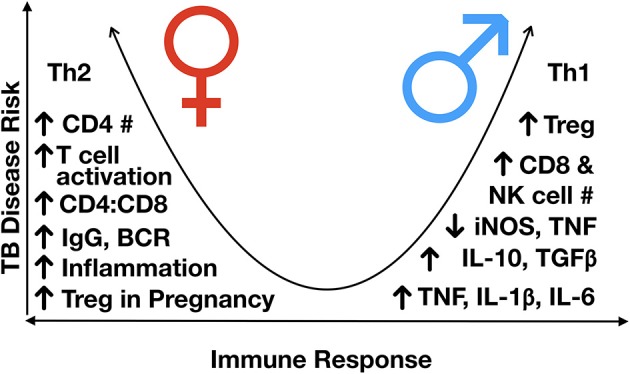
Immunological differences observed between males and females, post-puberty. TB disease risk increases as the immune response more heavily favors either Th2 or Th1 skewing, with a more balanced Th1/Th2 response having the lowest risk of disease progression. In general, males are Th1 skews and females Th2 skewed, although females have a higher inflammatory response to an exogenous stimulus, partly mediated by variable X-inactivation and the presence of estrogen response elements in many immune response genes, leading to higher responses once activated. BCR, B cell receptor; Ig, immunoglobulin; IL, interleukin; NK, natural killer; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; Th, T helper; TGFß, transforming growth factor-beta; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; #, number.
