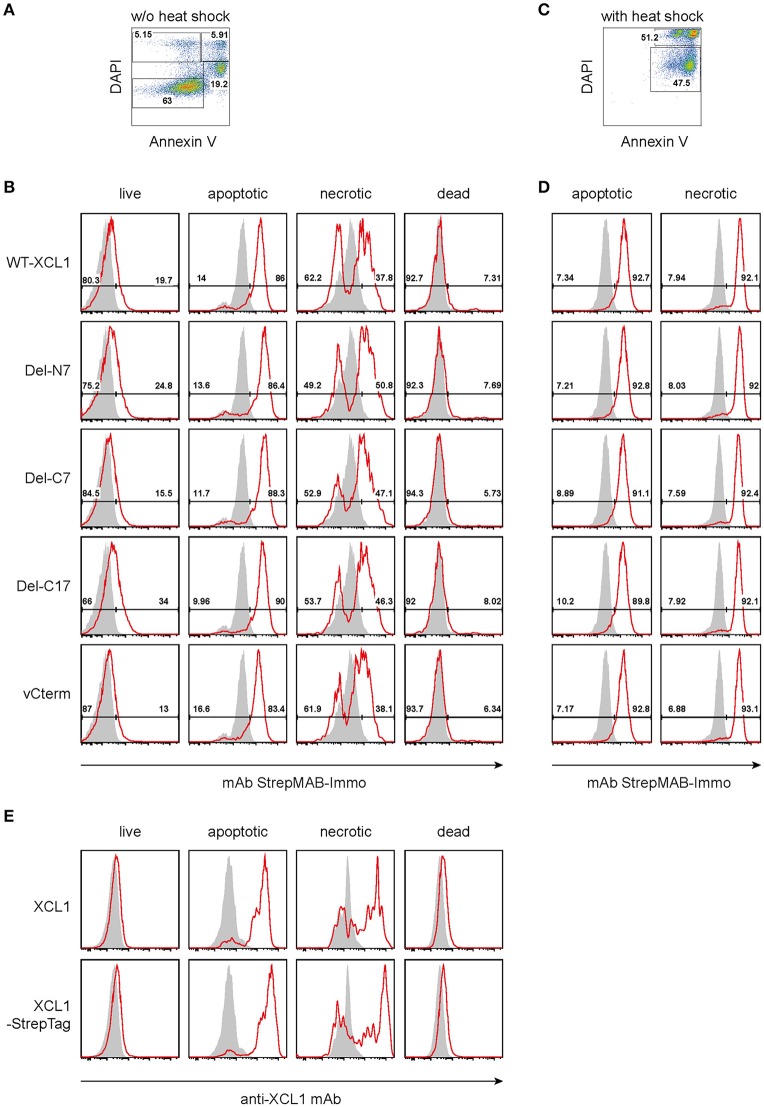
Figure 4.
Binding of XCL1-OVA and its variants Del-N7, Del-C7, Del-C17, and vCterm to apoptotic and necrotic cells. P3X63Ag8.653 cells were either (A,B,E) cultured at standard conditions without stress, or (C,D) subjected to thermal stress (52°C for 15 min, followed by culture overnight). For the last hour of culture, 1 μg of wt XCL1-OVA or one of its variants were added to the culture. For analysis, the cells were washed, and stained with DAPI and AnnexinV to subdivide the cells into “live” (Annexin−DAPI−), “apoptotic” (AnnexinV+DAPIlow), “necrotic” (Annexin+DAPI+), and “dead” (Annexin−DAPI+) cells. (A) Gating and (B) staining of cells without thermal stress, (C) gating and (D) staining of cells after thermal stress, using anti-StrepMAB-Immo for signal detection (red histograms); background staining with StrepMAB-Immo without any preincubation is shown in gray histograms. (E) P3X63Ag8.653 cells were cultured under identical conditions, without thermal stress. For the last hour of culture, 1 μg of wt XCL1 or XCL1-StrepTag were added to the culture. Washing of cells and gating with DAPI and AnnexinV was as described above. Signal was detected with mAb MTAC-311 specific for murine XCL1 (red histograms), background signals with MTAC-311, without any preincubation, are shown in gray. Concentrations of XLC1-variants are based on the XCL1-component of the respective construct.