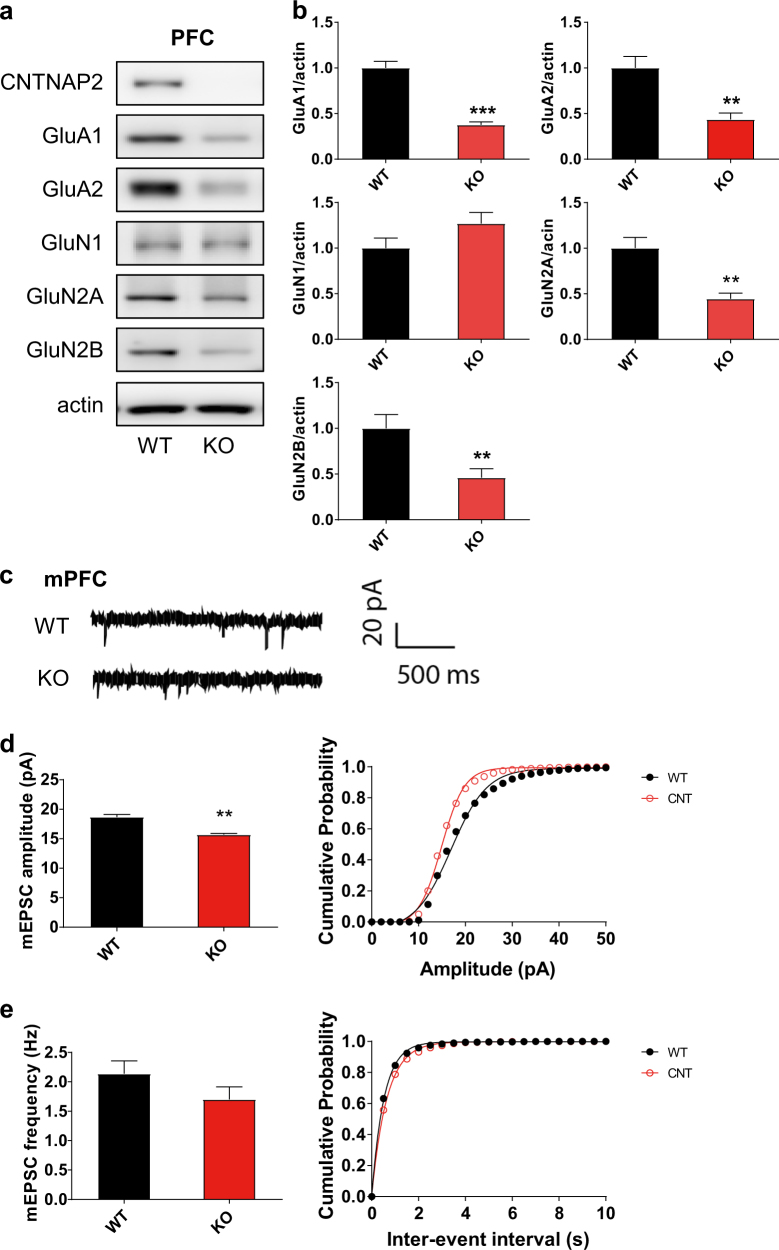
Fig. 1.
Decreased expression of ionotropic glutamate receptors and reduced excitatory synaptic transmission in Cntnap2 KO mice. To quantify the expression level of proteins and measure synaptic transmission western blotting (a, b) and whole-cell patch clamp recordings (c–e) were performed, respectively, using the medial prefrontal cortex. a, b The levels of ionotropic glutamate receptor subunits GluA1, GluA2, GluN2A, and GluN2B, but not GluN1, were significantly decreased in Cntnap2 knockout (KO) mice. c Representative traces of the miniature excitatory postsynaptic currents (mEPSCs). d, e The amplitude of mEPSCs, but not frequency, was significantly decreased in Cntnap2 KO mice. For western blotting: N = 8–10, and for electrophysiology: N = WT: 18, KO: 17. **, ***p < 0.01, 0.001, respectively vs. Con. In the graph, data are expressed as the mean ± standard error of the mean