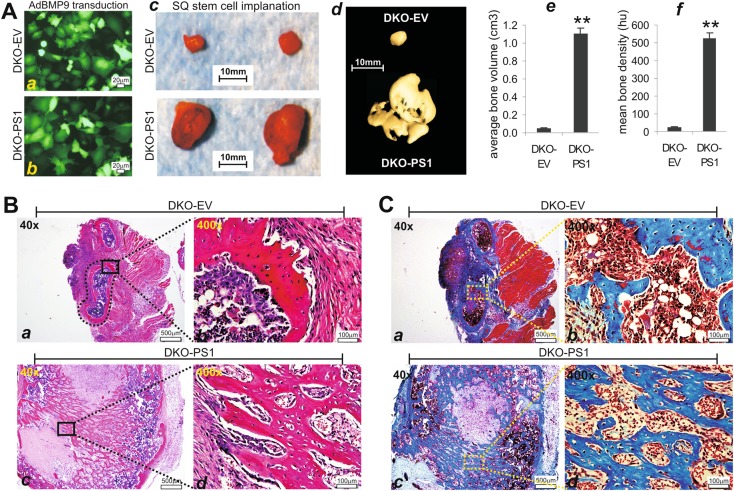
Fig. 6.
Genetic inactivation of Notch signaling blunts BMP9-induced ectopic bone formation in vivo. a Double-knockout PS1−/−/PS2−/− significantly blunts BMP9-induced ectopic bone formation in MSCs. Subconfluent DKO-EV or DKO-PS1 cells were infected with AdBMP9 or AdGFP for 24 h (a, b) and collected for subcutaneous injection into the flanks of athymic nude mice. At 4 weeks after implantation, bony masses were retrieved from BMP9 treatment groups while no masses were recovered from the GFP treatment group (c). The retrieved masses were fixed and subjected to µCT imaging (d), and the imaging data were further analyzed for average bone volume (e) and mean bone density (f). **p < 0.001. b H & E staining. The retrieved masses from BMP9-treated DKO-EV cells (a, b) and BMP9-treated DKO-PS1 cells (c, d) were decalcified and subjected to H & E staining. Representative results are shown. c Trichrome staining. The retrieved masses from BMP9-treated DKO-EV cells (a, b) and BMP9-treated DKO-PS1 cells (c, d) were decalcified and subjected to Trichrome staining. Representative results are shown