Fig. 6.
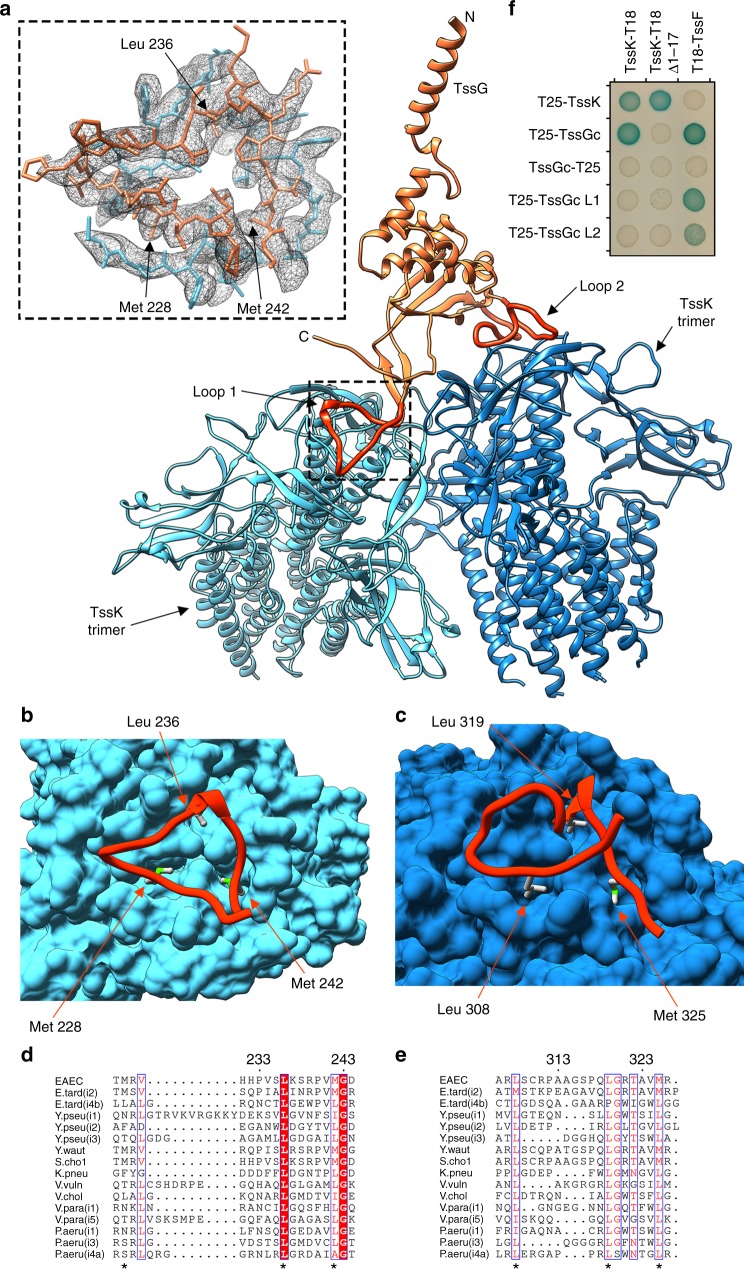
Attachment of TssK to the TssF–TssG heterotrimer. a Ribbon diagram showing that TssG loop 1 and loop 2 each anchor one TssK trimer to a baseplate wedge. The TssG N- and C-termini are labeled. The inset shows the atomic model built into the cryoEM density (gray mesh). b, c Zoomed-in view of the TssG loop 1-TssK b) and TssG loop 2-TssK c interactions. d, e Sequence alignment of TssG loop 1 d and loop 2 e from different bacterial species. In panels a, c, TssG is colored identically to Fig. 1 except for loop 1 and loop 2 that are rendered in orange/red and TssF is omitted for clarity. In b, c, TssK is rendered in surface representation. Hydrophobic residues that were mutated for the BACTH assay are labeled in a–c and indicated with * in d–e. EAEC: enteroaggregative Escherichia coli, E. tard (i2): Edwardsiella tarda (subtype i2), E. tard (i4b): Edwardsiella tarda (i4b), Y pseu (i1): Yersinia pseudotuberculosis (i1), Y pseu (i2): Yersinia pseudotuberculosis (i2), Y pseu (i3): Yersinia pseudotuberculosis (i3), Y waut: Yersinia wautersii, S. chol: Salmonella choleraesuis, K. pneu: Klebsiella pneumoniae, V. vuln: Vibrio vulnificus, V. chol: Vibrio cholerae, V. para (i1): Vibrio parahaemolyticus (i1), V. para (i5): Vibrio parahaemolyticus (i5), P. aeru (i1): Pseudomonas aeruginosa (i1), P. aeru (i3): Pseudomonas aeruginosa (i3), P. aeru (i4a): Pseudomonas aeruginosa (i4a). f Bacterial two-hybrid analysis of protein–protein interactions within the EAEC TssK–TssF–TssG complex. BTH101 reporter cells producing the indicated proteins or domains (TssGc: C-terminal domain of TssG, TssGc L1: C-terminal domain of TssG with the Met228Arg, Leu236Arg and Met242Arg substitutions, TssGc L2: C-terminal domain of TssG with Leu308Arg, Leu319Arg and Met325Arg substitutions, and TssK Δ1–17: TssK with deletion of the 17 N-terminal residues) fused to the T18 or T25 domain of the Bordetella adenylate cyclase were spotted on plates supplemented with IPTG and the chromogenic substrate X-Gal. Interaction between the two fusion proteins is attested by the dark blue color of the colony