FIG 1.
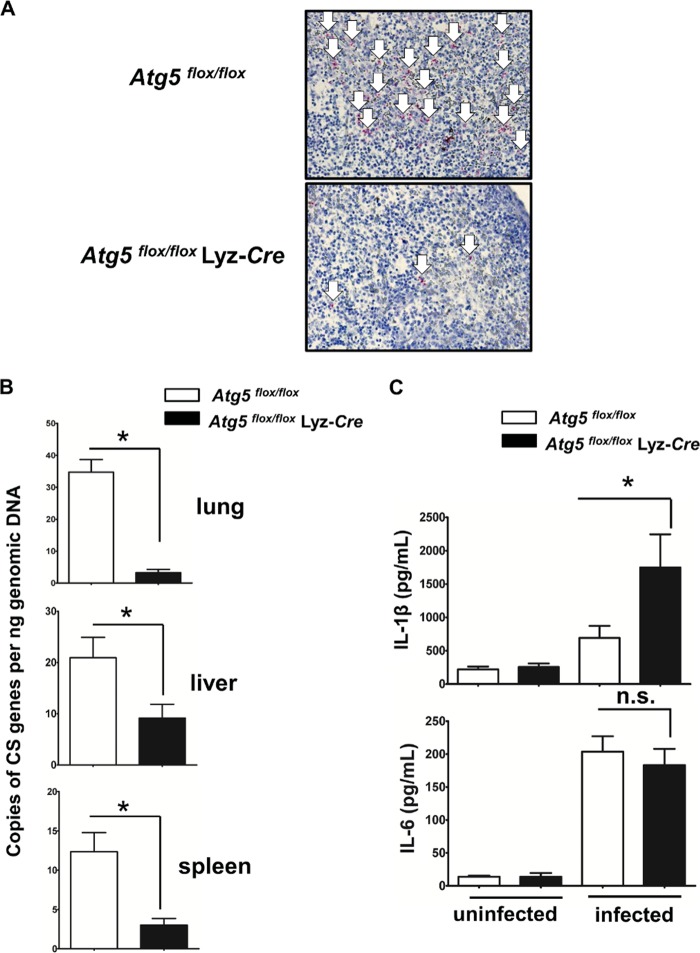
Atg5 in macrophages favors R. australis infection in vivo. Atg5flox/flox Lyz-Cre and Atg5flox/flox mice were inoculated with R. australis i.v. at a dose of 3 × 105 PFU per mouse. On day 4 p.i., the mice were euthanized. Mouse serum and tissues, including lung, liver, and spleen tissues, were collected. (A) The spleens of infected Atg5flox/flox Lyz-Cre and Atg5flox/flox mice were processed for immunohistochemical analysis of R. australis. Rickettsiae were stained red (as indicated by white arrows). (B) The rickettsial loads in mouse lung, liver, and spleen tissues were measured by quantitative real-time PCR. The number of rickettsial citrate synthase (CS) gene copies per nanogram of tissue genomic DNA represents the quantity of rickettsiae. (C) The serum levels of IL-1β and IL-6 in uninfected and infected mice were measured by Bio-Plex assay (Bio-Rad). Each mouse group included at least 3 to 5 mice. The data shown represent those from three independent experiments. *, P < 0.05; n.s., not significantly different.