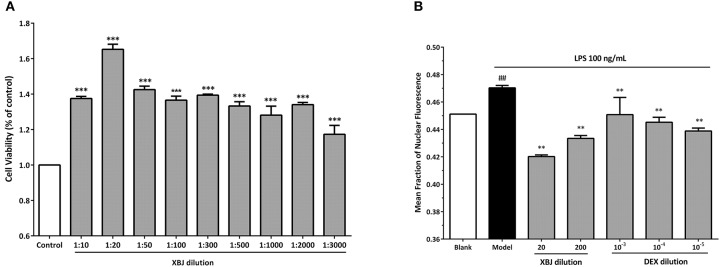
Figure 7.
XBJ inhibits NF-κB signaling in mouse macrophages without compromising viability. (A) The viability of 264.7 cells treated with different doses of XBJ using CCK8 assay. XBJ was diluted at 1/10, 1/20, 1/50, 1/100, 1/300, 1/500, 1/1,000, 1/2,000, and 3,000 ratios in the experiment. *: XBJ treated groups vs. control (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001). (B) Quantification of NF-κB nuclear translocation by an Operetta high-content florescent imaging system (Perkin Elmer) after LPS stimulation in the presence of different doses of XBJ or DEX. XBJ was diluted in 1/20 and 1/200. Dexamethasone (DEX) was used as a positive control in the experiment. 10−3, 10−4, and 10−5mM of DEX were used to treat 264.7 cells. Cells were treated with LPS for 30 min before the indicated doses of XBJ or DEX were added. Then, the cells were incubated for 12 h before the fixation, antibody staining and imaging. #: Blank vs. model. *: Treatment groups vs. model (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; #P < 0.05; ##P < 0.01; ###P < 0.001).