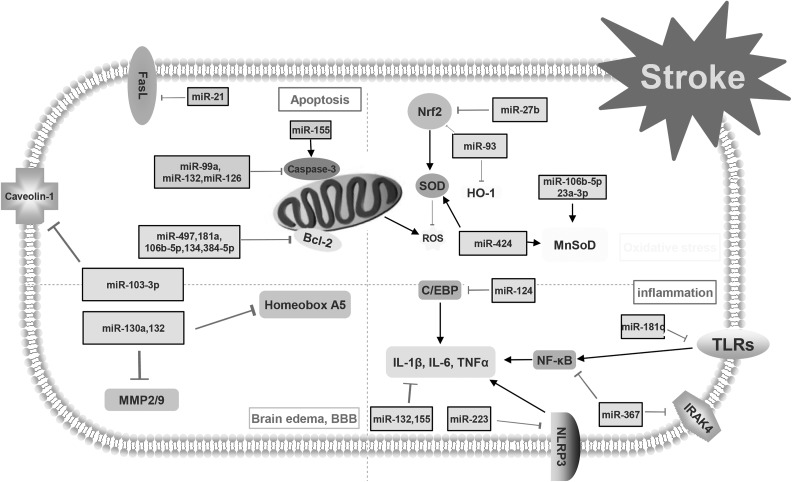
Fig 1.
This figure demonstrates the mechanisms of post-stroke pathophysiology. Apoptosis, neuroinflammation, oxidative stress and blood–brain barrier (BBB) disruption with brain edema are the main avenues that research tries to focus on to decrease the consequences of stroke. Different types of microRNAs and their targets are involved in the pathophysiology of stroke.
C/EBP: CCAAT/enhancer binding protein; FasL: Fas ligand; HO-1: hemeoxygenase-1; MMP: matrix metalloproteinase; NF-κB: nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; ROS: reactive oxygen species; SOD: superoxide dismutase; TLR: Toll-like receptor.