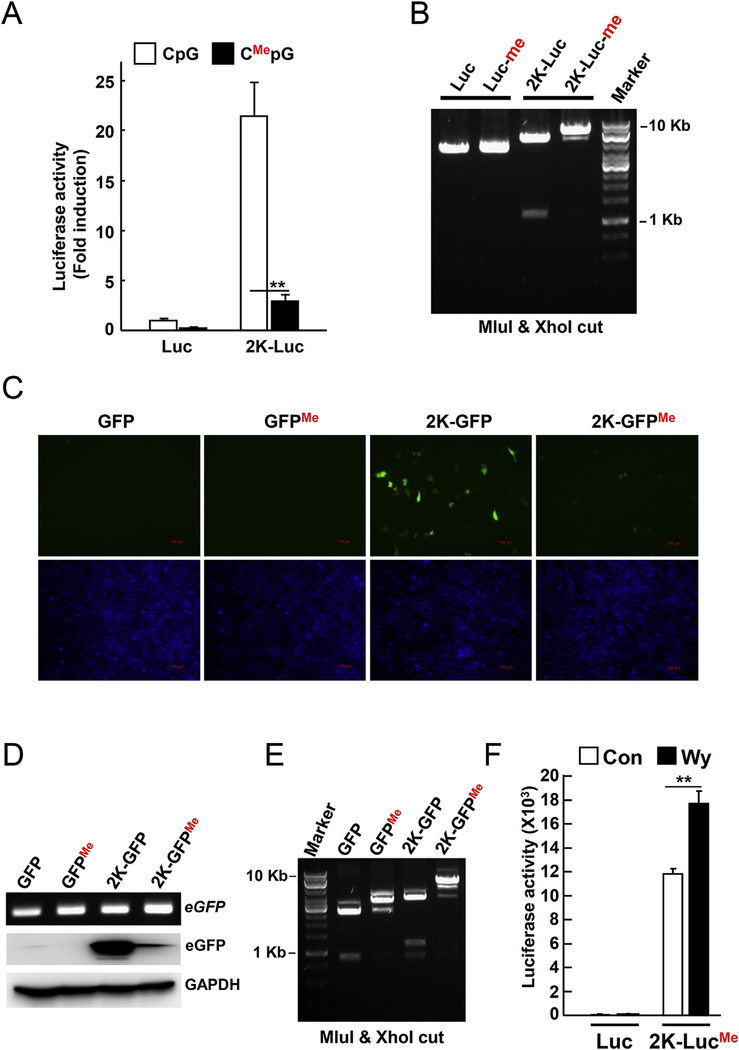
Fig. 4. Wy-14,643 increases the Gadd45b-luciferase activity by abolishing the CpG methylation.
(A) To demonstrate that CpG methylation could suppress gene expression, the Gadd45b-luciferase construct was incubated with CpG methyltransferase enzyme (M.SssI) to introduce methyl group in the cytosine of CpG and followed by reporter assay. Hepa1c1c7 cells were transfected with control or CpG methylated Gadd45b-luciferase construct (2K-luc) for 24 h (B) CpG methylation of the Gadd45b-luciferase construct was tested by electrophoresis following MluI and Xho restriction digestion. (C) Hepa1c1c7 cells were transfected with CpG methylated Gadd45b-eGFP reporter plasmid for 24 h. Green indicates the eGFP expression. Blue represents nuclei after Hoechst 33,342 staining. (D) PCR to confirm transfection by detecting GFP was performed on transfected samples from (C). eGFP expression was detected by Western blotting. GAPDH was used as a loading control. (E) CpG methylation of Gadd45b-eGFP constructs was tested by gel electrophoresis following MluI and Xho restriction digests. (F) To confirm if Wy-14,643 reversed the effect of CpG methylation of Gadd45b-luciferase in vivo, the constructs (10 μg) were transfected into mice by mouse-tail vein injection. 2K-luc, Gadd45b-luciferase construct (2 Kbp size); Me, methylated; **, p < 0.001. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)