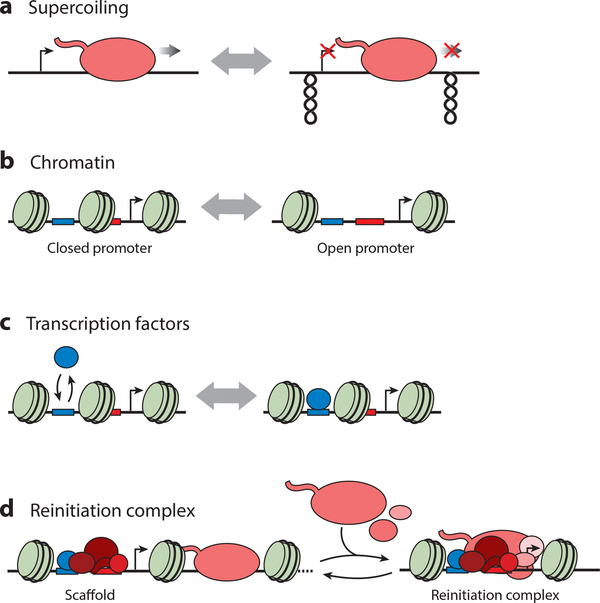
Figure 4:
Different hypotheses that have been proposed as a mechanism for transcriptional bursting. (a) Supercoiling buildup during transcription can result in inhibition of initiation and elongation and has to be released before transcription can resume. (b) Nucleosome positioning or binding in promoter regions may affect the accessibility of transcriptional regulators to DNA binding sites. (c) The binding dynamics of a specific regulatory factor, such as a gene-specific transcription factor, can determine bursting if initiation takes place as long as the factor is bound to DNA. (d) After initiation, several general transcription factors can remain bound to the promoter, forming a scaffold for rapid reinitiation and firing of multiple polymerases at the same time.