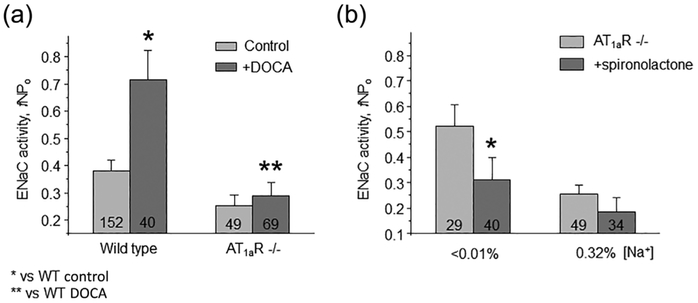
FIGURE 5.
AT1aR deletion impairs regulation of ENaC activity by mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) signaling. (a) Summary graph of averaged total ENaC activity, fNPo in Wild type and AT1aR −/− mice in the control and after systemic Deoxycorticosterone acetate (DOCA) injections for 3 consecutive days to maximally stimulate MR. *significant increase versus Wild type control; **significant decrease versus Wild type + DOCA. (b) Summary graph comparing averaged total ENaC activity, fNPo in AT1aR −/− mice kept on low (<0.01% Na+) and control (0.32% Na+) salt intake in the absence (light gray) and presence (dark grey) of concomitant treatment with MR antagonist spironolactone (30 mg/kgBW) in drinking water, respectively. *significant decrease versus AT1aR −/− low salt