Figure 5. MiR-106a deficiency promotes anti-inflammatory T cell induction.
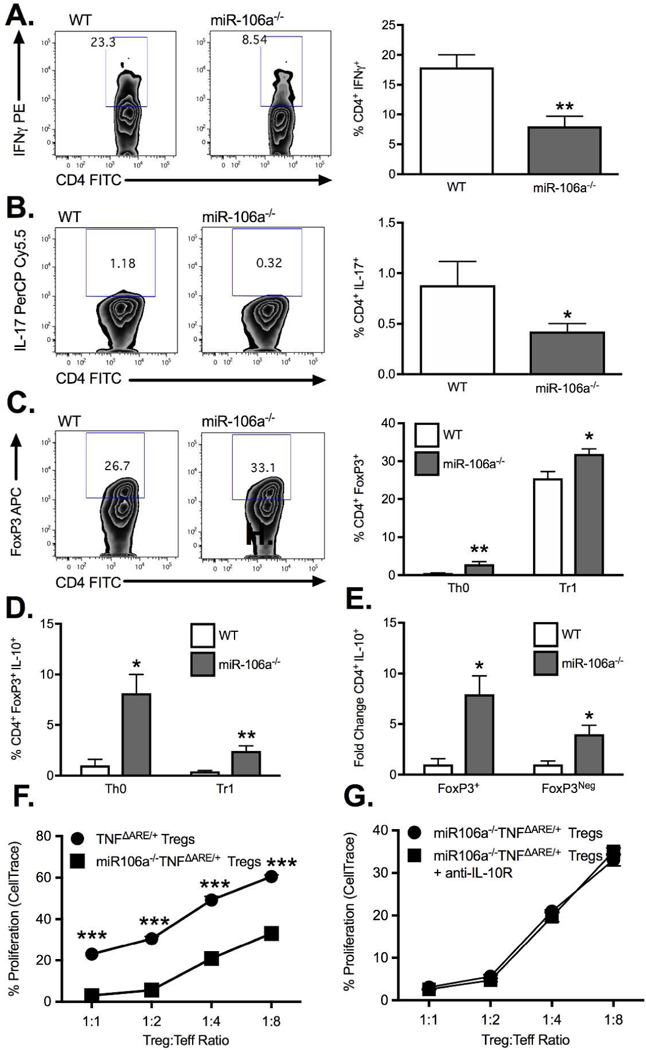
Under Th0 conditions, isolated CD4+CD25Neg cells from miR-106a−/− mice displayed a significant decrease in expression of (A) IFN and (B) IL-17 as well as an increase in (C) FoxP3 relative to WT controls. In the presence of TGFβ, miR-106a−/− CD4+CD25Neg cells underwent significantly greater Treg conversion compared to WT (C) with greater IL-10 production under both conditions (D). (E) The fold change increase in IL-10 production by miR-106a−/− cells under Th0 conditions was greater in FoxP3+ but also occurred in FoxP3Neg cells. (F) Isolated Tregs from miR-106a−/−TNFΔARE/+ mice displayed significantly greater in vitro suppressive function relative to TNFΔARE/+ alone. (G) Enhanced suppressive function was maintained with antibody blockade of IL-10R signaling. Results represent mean ± SEM for four technical replicates from three independent studies. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
