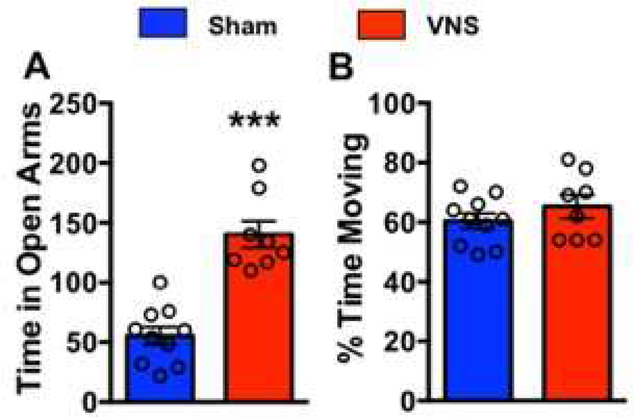
Figure 5. VNS reduces anxiety.
Rats were given one non-contingent train of VNS or sham stimulation in their home cage. Ten minutes later, they were removed from their home cage and placed on the elevated plus maze (EPM). VNS-treated rats spent significantly more time in the open arms of the EPM when compared to sham-treated rats (p=2.1×10−3), indicating a VNS-induced reduction in anxiety. The percent of time spent moving during EPM testing was similar between groups, indicating no general locomotor effect.