Figure 1.
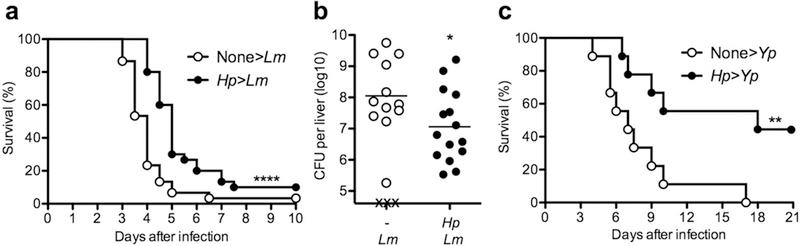
Helminth infection provides protection against subsequent systemic and enteric bacterial infection. B6 WT mice were either uninfected or infected by gavage with 200 larvae of Hp, and cured with an antihelminthic after 2 weeks. (a and b) One week later, mice were challenged intraperitoneally with 2.5×106 CFU of the Gram-positive bacterium Lm. (a) Survival was monitored in 12 hr intervals. Data were pooled from 3 independent experiments (n=30 per group). (b) Bacterial burden in the liver was determined at day 3 after Lm challenge. Data were pooled from 2 independent experiments. Solid bar depicts mean. X indicates individual mice that had succumbed to infection prior to analysis. (c) One week after drug cure, mice were challenged by gavage with 5×109 CFU of the Gram-negative bacterium Yp. Survival was monitored in 12 hr intervals. (n=9 per group). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ****P < 0.0001 by log rank test (a and b) or Student’s t test (b).
