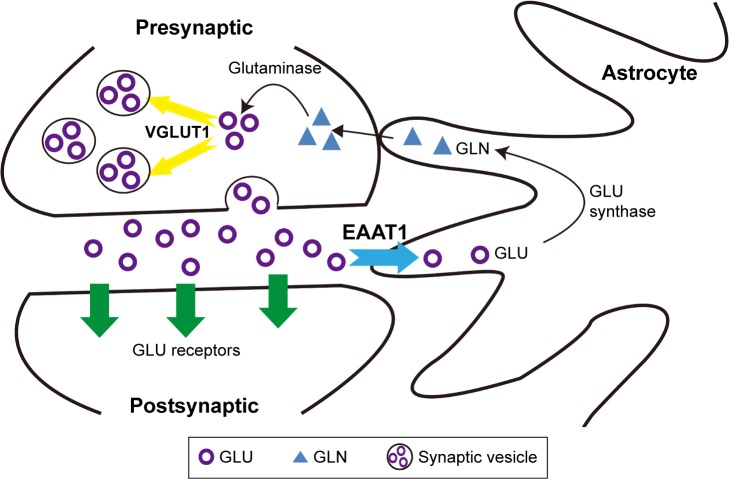
Figure 1.
Simple diagram of glutamate transport.
Notes: GLU released by vesicular exocytosis is uptaken from synaptic cleft by EAAT1, which is metabolized to GLN through the action of glutamate synthase. GLN then is transported back into neurons, converted to GLU through the action of glutaminase, and sequestered into synaptic vesicles by VGLUT1.
Abbreviations: EAAT1, excitatory amino acid transporter 1; GLN, glutamine; GLU, glutamate; VGLUT1, vesicular glutamate transporter 1.