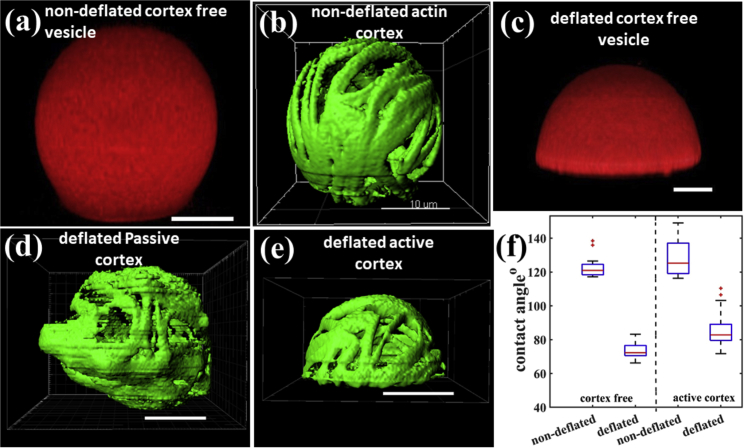
Figure 4.
(a and b) Cortex-free and passive cytoskeletal vesicle in the weakly adhered or nondeflated state, respectively. (c) The cortex-free vesicle adopts a spherical cap shape after deflation, a signature of strong adhesion. (d and e) The passive and active vesicles, respectively after deflation. The deformation leads to undefined shapes in the case of the passive vesicles and spherical cap shape in active vesicles. (f) The almost equal difference in the contact angle between nondeflated and deflated state for cortex-free and the active cortex vesicles shows that the active vesicle can use the excess membrane area developed by deflation in reducing the contact angle to spread on the surface. 20 vesicles were imaged for each vesicle type for the box-and-whisker diagram. The method we used to estimate the contact angle is shown in the Fig. S4. Scale bars, 10 μm. To see this figure in color, go online.