FIGURE 2.
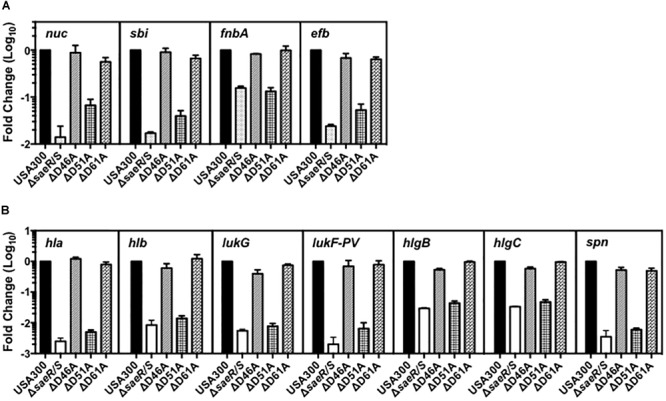
Aspartic acid residue 51 of SaeR is important for the transcription of numerous virulence genes in USA300. Taqman® RT-PCR analysis of USA300, an isogenic deletion mutant of saeR/S in USA300 (USA300ΔsaeR/S), and USA300 genomic point mutants that confer aspartic acid to alanine substitutions at SaeR residue 46 (ΔD46A), 51 (ΔD51A), or 61 (ΔD61A) during growth in vitro. Transcriptional analysis was performed at (A) mid-exponential growth for nuclease (nuc), the second binder of IgG (sbi), fibronectin-binding protein A (fnbA), and the extracellular fibrinogen-binding protein (efb) or at (B) early-stationary growth for γ-hemolysin (hla), γ-hemolysin (hlb), leukocidin subunit G (lukG), the Panton-Valentine leukocidin subunit F (lukF-PV), γ-hemolysin component B (hlgB),γ-hemolysin component C (hlgC), and the staphylococcal peroxidase inhibitor (spn). All panels show the mean ± SEM of at least two separate experiments and are presented as fold change relative to USA300 wt.
