FIGURE 6.
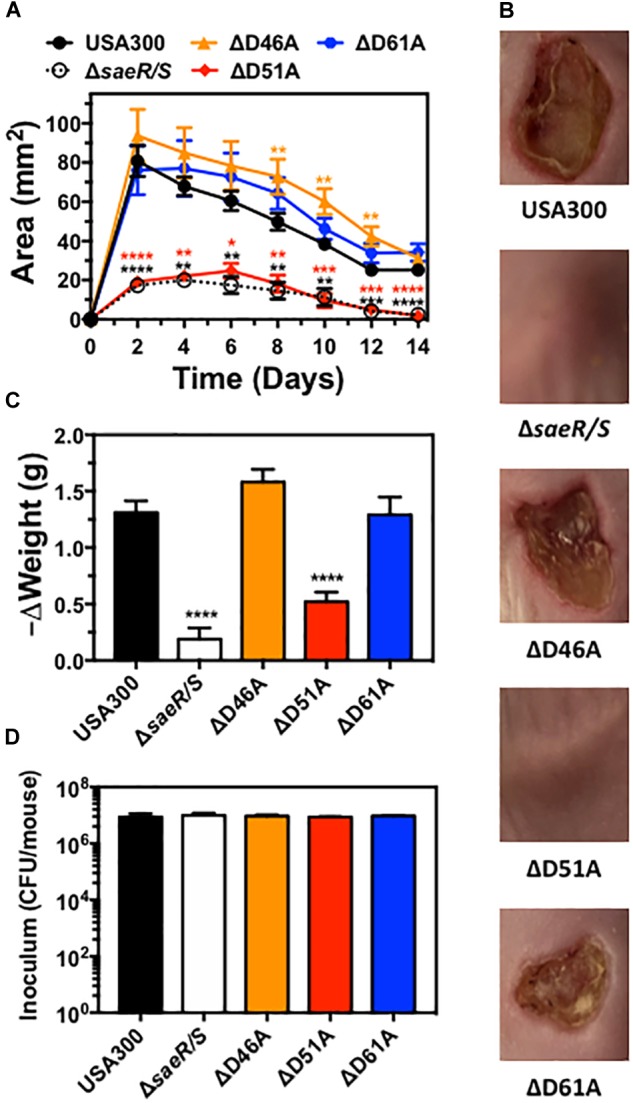
Aspartic acid residue 51 of SaeR significantly influences the pathogenesis of murine soft-tissue infections caused by USA300. (A) Area of soft-tissue infection caused by USA300, an isogenic deletion mutant of saeR/S in USA300 (ΔsaeR/S), or USA300 with an aspartic acid to alanine substitution at SaeR residue 46 (ΔD46A), 51 (ΔD51A) or 61 (ΔD61A). (B) Representative images of soft-tissue infections from experiments in panel (A) on day 6 post-inoculation. (C) Change in the weight of mice during experiments in panel (A) between days 0 and 2 post-inoculation. (D) Inoculum of each strain given to mice in panels (A-C). Panels (A), (C), and (D) show the mean ± SEM of two independent experiments. ∗P ≤ 0.05, ∗∗P ≤ 0.01, ∗∗∗P ≤ 0.001 and ∗∗∗∗P ≤ 0.0001 relative to USA300 as determined by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test.
