Fig. 10.
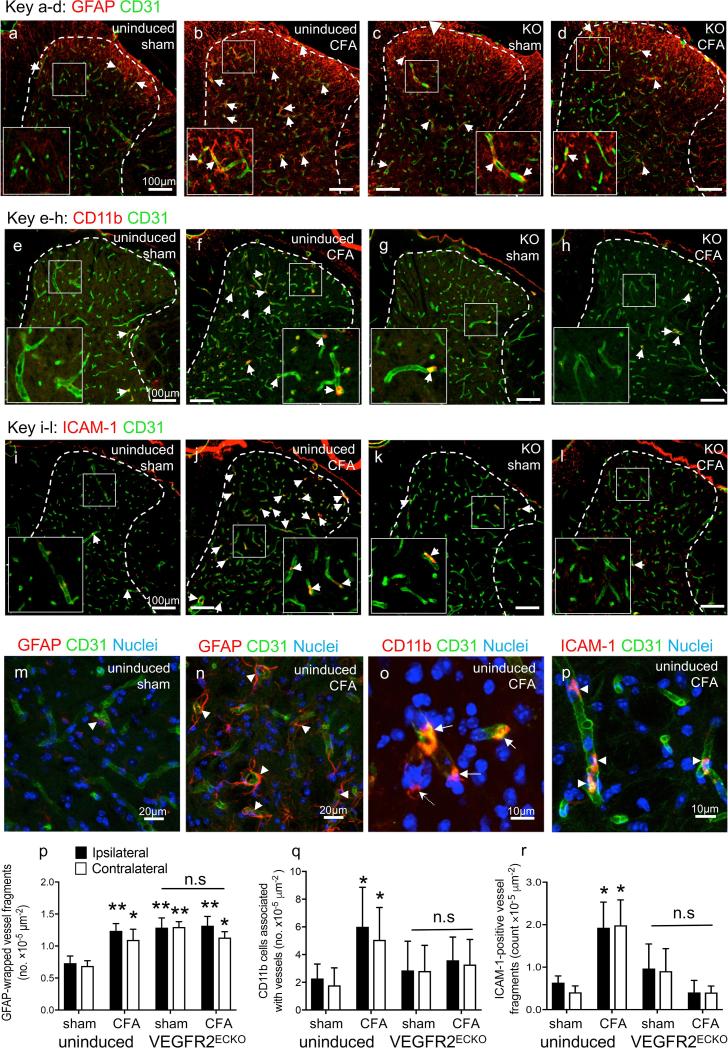
VEGFR2ECKO inhibited glio-vascular activation in the dorsal horn of CFA treated mice. Peri-articular CFA caused an significant increase in the number of dorsal horn CD31+ vessels associated with GFAP+ reactive astrocytic foot processes (glio-vascular response) compared with sham in uninduced mice (a,b, quantification in p). There was a significant increase in the number of vessels associated with GFAP+ astrocytic foot processes in sham-treated VEGFR2ECKO compared with sham-treated uninduced controls, however CFA treatment in VEGFR2ECKO mice did not significantly increase this further (c,d, quantification in p). CFA caused a significant increase in the number of CD11b+ cells associated with CD31+ vessels and the number of ICAM-1+ vessel structures in uninduced mice compared with sham (e,f,i,j quantification in q&r) but the same effects were not observed in VEGFR2ECKO (g,h,k,l quantification in q&r). Higher magnification images of GFAP+ reactive astrocytic end feet (m, n, arrowheads denote GFAP+/CD31+ vessel structures), CD11b+ cells associated with vessel (n, arrows denote CD11b+ cells associated with CD31+ vessel structures, dotted arrow denotes a parenchyma CD11b+ cell) and ICAM-1+ vessels (o, arrowheads denote ICAM-1+/CD31+ vessel structures). Three statistical analyses were performed: 2-way ANOVA + Bonferroni multiple comparisons test: vs. uninduced sham con *p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01; KO CFA vs KO sham control – no significance; contra vs. ipsi of respective group – no significane; n = 3–6. Data displayed as mean ± SD.