FIGURE 3.
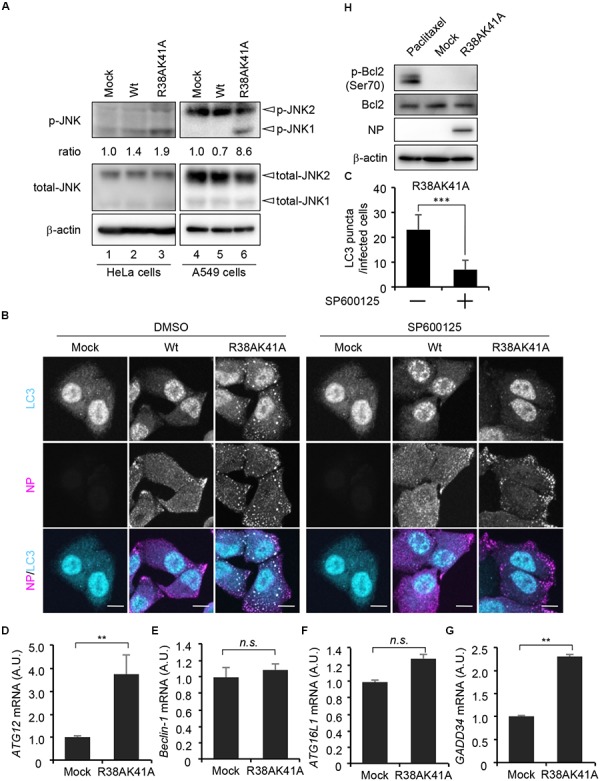
JNK1 signaling pathway is required for the autophagosome formation in R38AK41A-infected cells. (A) HeLa cells were infected with Wt or R38AK41A virus at MOI of 3. At 4 h post-infection, cell lysates were subjected to western blotting assays with anti-phospho-JNK, anti-JNK, anti-NP, and anti-β-actin antibodies (lanes 1–3). The p-JNK/β-actin ratios determined by FUSION system (Vilber-Lourmat) are shown underneath the p-JNK blot. The JNK1 activation in A549 cells was also examined (lanes 4–6). (B,C) HeLa cells were infected with either Wt or R38AK41A virus at MOI of 3. At 4 h post-infection, cells were treated for 6 h with SP600125, a JNK inhibitor, and then subjected to the indirect immunofluorescence assays with anti-LC3 (cyan) and anti-NP (magenta) antibodies. Scale bar, 10 μm. The average number of LC3 puncta in R38AK41A-infected cells treated with or without SP600125 and standard deviations determined from three independent(experiments were shown in panel C (n > 100). The statistical significance was determined by Student’s t-test, ∗∗∗P < 0.001. (D–G) HeLa cells were infected with R38AK41A virus at MOI of 3. At 4 h post-infection, total RNAs were isolated and subjected to quantitative RT-PCR with primer sets specific for ATG12 (C), Beclin-1 (D), ATG16L1 (E), and GADD34 (F) mRNAs. The mean value and standard deviations obtained from three independent experiments are shown. ∗∗P < 0.01 by Student’s t-test. (H) HeLa cells were infected with R38AK41A virus at MOI of 3. At 4 h post-infection, the cell lysates were subjected to western blotting assays with anti-phospho-Bcl-2, anti-Bcl-2, anti-NP, and anti-β-actin antibodies. HeLa cells were treated with 10 nM paclitaxel for 12 h as a positive control for phosphorylated Bcl-2 (lane 1).)
