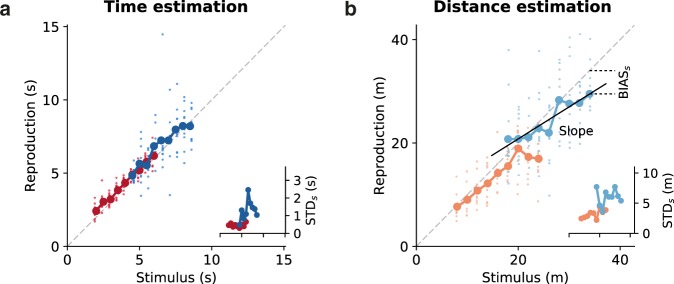
Figure 2.
Time and distance reproductions of an example child. Individual reproduced values for stimulus interval (a) or distance (b) are given as small dots and averages for each stimulus as large dots connected by a solid line. Colors identify stimulus distributions (cf. Fig. 1b). Gray dashed lines mark bisecting lines. The insets give the standard deviation STDs for each stimulus. The x-axis is the same as in the main panel. During time estimation reproduction is veridical in this participant. For distance estimation, regression effects are visible in particular for the long stimulus range. An increased standard deviation for larger stimuli can be observed for both time and distance estimation. In (b) the bias for the largest stimulus BIASs and a linear fit (black solid line) from which we extracted the slope are illustrated.