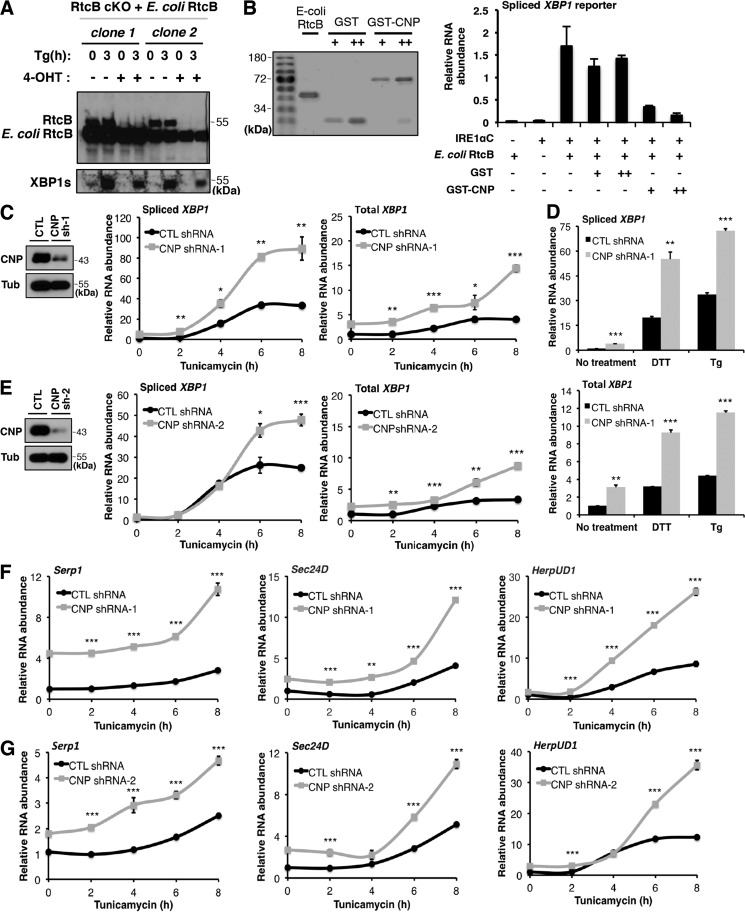
Figure 4.
CNP inhibits RtcB-mediated XBP1 splicing in vitro and in vivo. A, E. coli RtcB rescued mammalian XBP1 splicing when endogenous RtcB was depleted. B, recombinant CNP inhibited XBP1 splicing in vitro. Coomassie Blue staining shows affinity-purified E. coli RtcB, GST, and GST-CNP proteins. The purified proteins were diluted to have similar protein concentrations and added to the in vitro splicing reaction of an XBP1u intron–containing in vitro transcribed RNA as described in Lu et al. (18). The RNA products were purified and analyzed by RT-qPCR. The results were normalized to the total reporter RNA levels in the reactions. C, knockdown of CNP by shRNA-1 (sh-1) in HEK293T cells. CNP down-regulation was verified by Western blotting. Upon ER stress induction by tunicamycin for the indicated times, spliced and total XBP1 mRNA levels were quantified by RT-qPCR. D, as in C, ER stress was induced in CNP knockdown cells by DTT for 2 h and thapsigargin (Tg) for 3 h. Spliced (top panel) and total (bottom panel) XBP1 mRNA levels were quantified. E, to control for off-target effects of RNAi, the experiment in C was repeated with a different shRNA (CNP shRNA-2 (sh-2)). F and G, up-regulation of XBP1 target genes in CNP knockdown cells. Expression of previously identified XBP1 targets (Serp1, Sec24D, and HerpUD1) were analyzed by RT-qPCR. GAPDH was used for normalization. The results are shown as mean ± S.E. (error bars) and were subjected to two-tailed t tests. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001. CTL, control.