Figure 6.
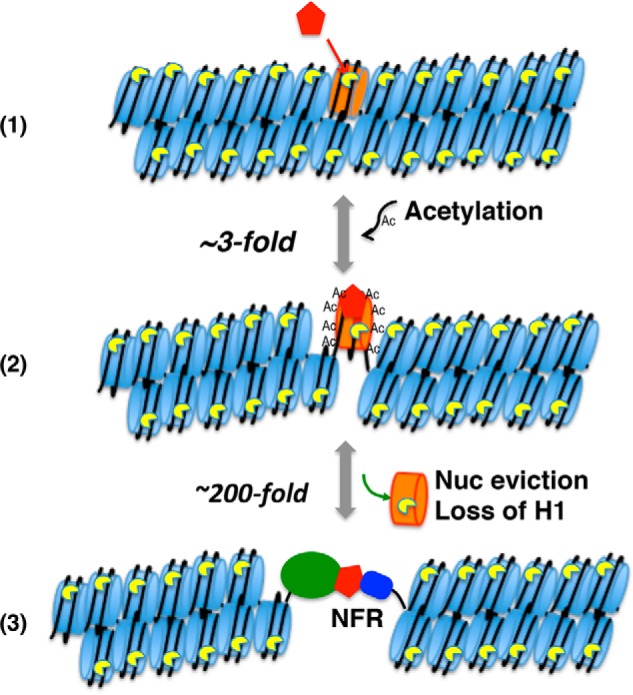
Factors affecting linker DNA accessibility. A pioneer factor (red) binds the target nucleosome (orange) in closed chromatin and recruits histone acetyltransferases (1), resulting in ∼3–4-fold increase in accessibility to the linker DNA (2). The acetylation and increased accessibility allow the recruitment of additional factors, resulting in nucleosome (Nuc) and H1 displacement (3) and a ∼200-fold increase in accessibility to the DNA. Note that some pioneer factors displace H1 directly, resulting in accessible nucleosomes (68). Note that the NFR was still digested 4 times slower than naked DNA or a nucleosome ligated to two naked 25-mer templates, indicating that the folding of the remainder of the nucleosome arrays still provides significant impediment (21).
