Figure 2.
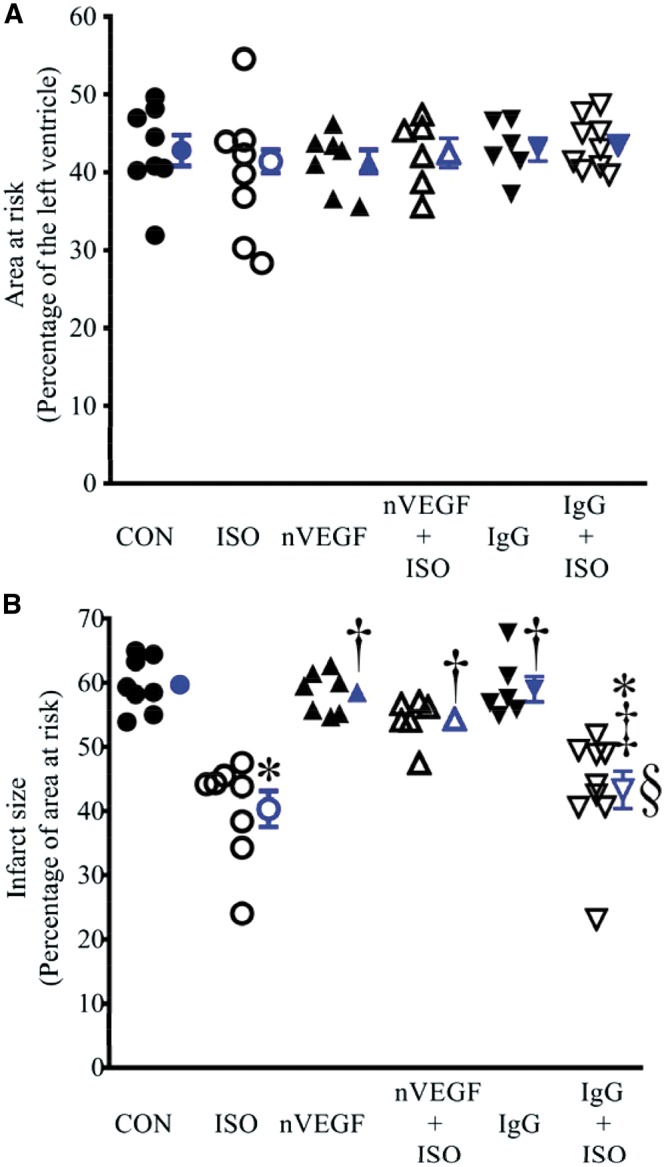
Isoflurane (ISO)-induced decrease in infarct size was blocked by neutralizing anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (nVEGF) in rats subjected to myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion injury. (A) Area at risk expressed as a percentage of the left ventricle; (B) infarct size expressed as a percentage of area at risk. The rats were subjected to 30 min of coronary artery occlusion followed by 2 h of reperfusion (control, CON). Isoflurane (ISO) was administered for 30 min followed by a period of 15 min washout prior to coronary artery occlusion. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn’s test was used to analyse multiple group comparisons. *P < 0.05 vs. CON (control); †P < 0.05 vs. ISO; ‡P < 0.05 vs. nVEGF + ISO; §P < 0.05 vs. IgG (n = 6–9 rats/group).
