Fig. 2.
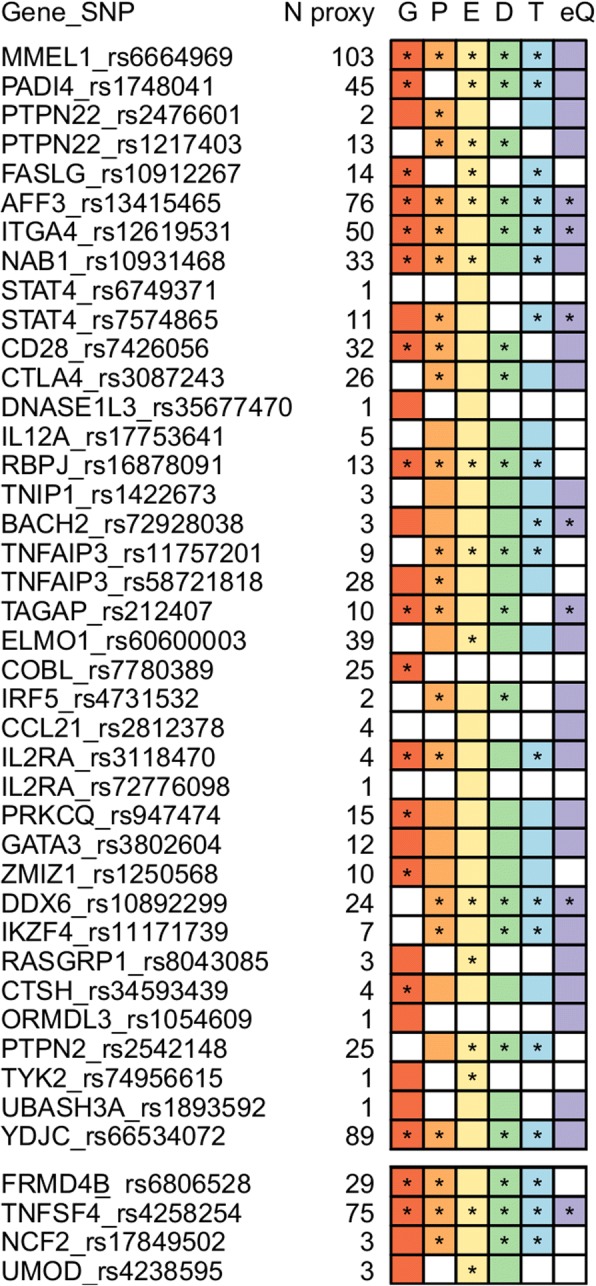
Functional annotation of 38 pleiotropic polymorphisms (p < 5 × 10–8 in the subset-based meta-analysis) and four single-disease associated variants (p < 5 × 10–6 in the subset-based meta-analysis and p < 5 × 10–8 in disease-specific meta-analyses). Haploreg v4.1 was used to explore whether lead SNPs, and their proxies (r2 ≥ 0.8), overlapped with different regulatory datasets from the Roadmap Epigenomics project, the ENCODE Consortium and more than ten eQTL studies in immune cell lines, cell types relevant for each specific disorder and/or whole blood. Colors denote both lead and proxy SNPs overlapping with the different regulatory elements analyzed: G (red): conserved positions (Genomic Evolutionary Rate Profiling, GERP); P (orange): promoter histone marks; E (yellow): enhancer histone marks; D (green): DNase I hypersensitive sites (DHS); T (blue): transcription factor binding sites (TFBSs); eQ (purple): expression quantitative trait loci (eQTL). Functional annotations overlapping with proxy SNPs are marked with an asterisk. N proxy, number of proxy SNPs for each lead variant. The different loci are annotated with the candidate gene symbol
