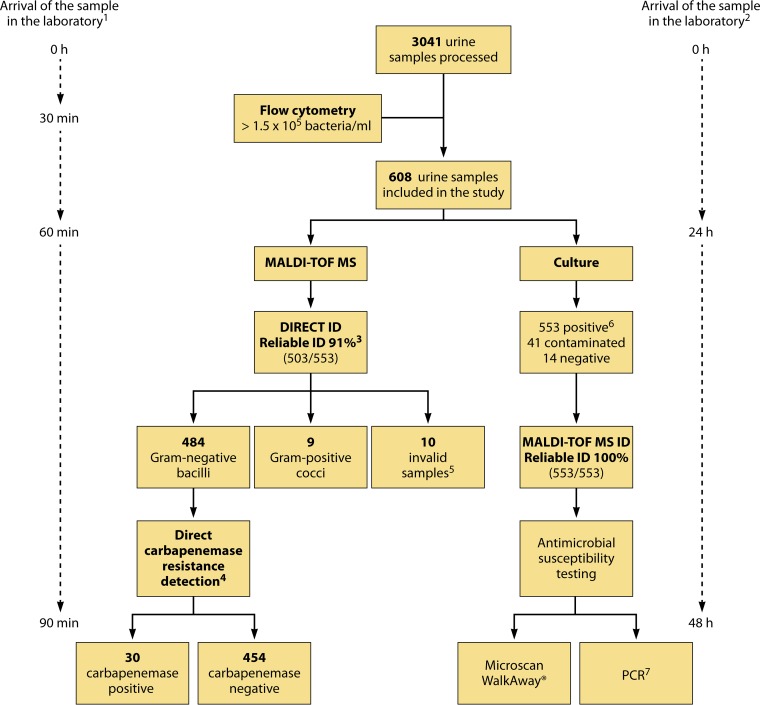
FIG 1.
Workflow diagram showing the detection of carbapenemase activity directly from clinical urine samples. (Republished from reference 44 with permission of the British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy.) 1, expected time for direct identification of bacteria and detection of carbapenemase susceptibility in urine samples by MALDI-TOF MS. 2, expected time for identification of bacteria and detection of carbapenemase susceptibility in urine samples by routine microbiological processing. 3, according to the manufacturer, a score of <1.7 indicates unreliable identification, a score of between 1.7 and 2.0 indicates genus identification, and a score of ≥2.0 indicates species identification. 4, carbapenemase activity was detected directly in urine samples and was measured by MALDI-TOF MS and automated spectrum interpretation. LogRQ values below 0.2 represent negative strains, values above 0.4 indicate carbapenemase activity, and values between 0.2 and 0.4 represent an ambiguous hydrolysis pattern. 5, invalid samples were those in which the amount of pellet obtained was not sufficient to carry out direct identification of bacteria and the carbapenem resistance assay. 6, urine samples were considered positive with ≥104 CFU/ml of one microorganism, whereas samples with two or more microorganisms were considered contaminated. 7, Gram-negative bacilli in positive urine samples were characterized by PCR and further sequencing of carbapenemase genes.