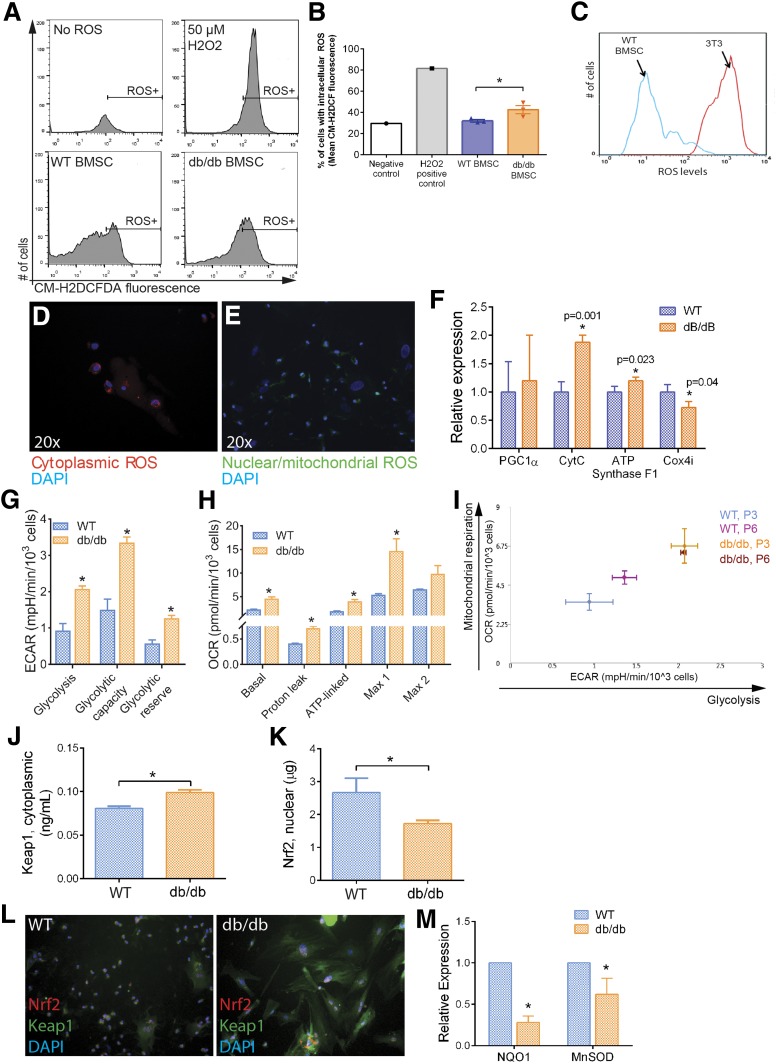
Figure 2.
Nrf2/Keap1 pathway affected in altered dBMSCs. A: Detection of intracellular ROS using CM-H2DCFDA. ROS induces deacetylation of cell-permeant CM-H2DCFDA to fluorescent DCF (Ex/em 492–495/517–527 nm) that is trapped. B: Quantification of intracellular ROS. C: Comparison of ROS levels between WT-BMSCs and stromal cells using CM-H2DCFDA. D and E: Fluorogenic detection of ROS in cytoplasm (red) and nuclei and mitochondria (green). F: Gene expression of oxidative phosphorylation genes. G: Glycolytic indices, derived from Seahorse Mito Stress analysis. H: Mitochondrial respiratory indices, derived from Seahorse Mito Stress analysis. I: Energy map of WT and dBMSCs, comparison between P3 and P6. J and K: ELISA of nuclear Nrf2 and cytoplasmic Keap1 using lysates of WT and dBMSCs. L: Immunofluorescence of Nrf2 and Keap1 proteins in WT and dBMSCs. Magnification is 20×. M: Relative expression of Nrf2 target genes in WT vs. dBMSCs. Data represented as mean ± SD; n ≥ 3. *P < 0.05. See also Supplementary Fig. 2. ECAR, extracellular acidification rate; OCR, oxygen consumption rate.