Figure 3.
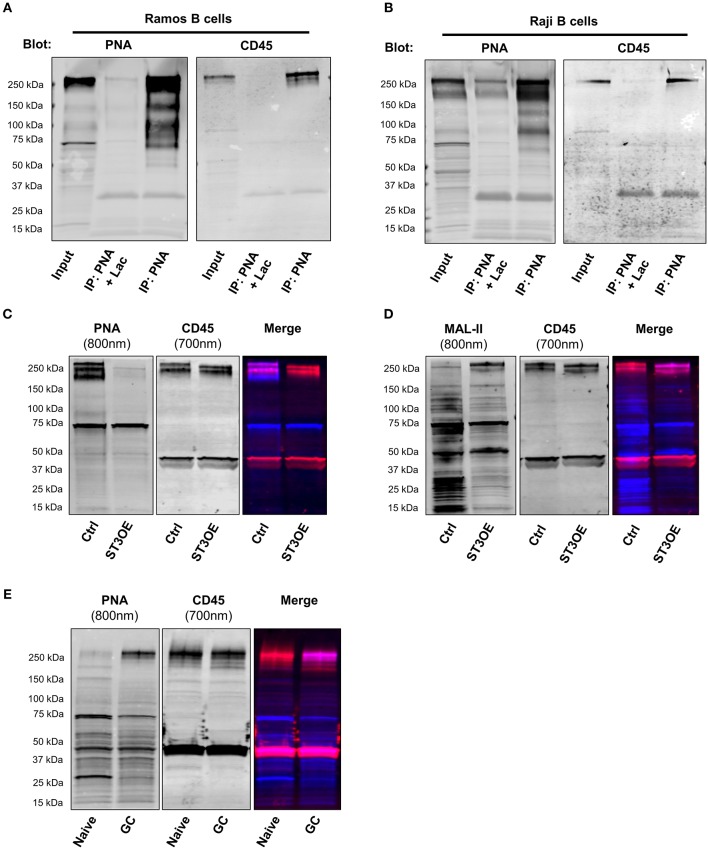
CD45 is a major glycoprotein bearing PNA-reactive O-glycans on B cells. (A) Immunoprecipitation (IP) with PNA-agarose beads from lysates of a GC-derived Burkitt lymphoma B cell line (Ramos), followed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblot with either PNA (left) or CD45 antibody (right). As a negative control, IP was also performed in the presence of a sugar inhibitor, lactose (Lac; middle lane). (B) IP and immunoblot of PNA-binding proteins of lysates from a second GC-derived Burkitt lymphoma B cell line (Raji), as in (A). (C) Western blot analysis of PNA binding to Ramos vector control and ST3Gal1OE lysates (left; 800 nm fluorescence channel) followed by immunoblot with CD45 antibody (middle, 700 nm fluorescence channel). Right, merged. (D) Western blot analysis of staining of Ramos vector control and ST3Gal1OE lysates with MAL-II lectin (left; 800 nm fluorescence channel) followed by CD45 antibody (middle, 700 nm fluorescence channel). Right, merged. (E) Immunoblot of lysates from magnetically-enriched naïve and GC B cells with PNA (left; 800 nm fluorescence channel) followed by CD45 antibody (middle, 700 nm fluorescence channel). Right, merged. Data from (A,B) are from one experiment each showing similar results using three different B cell lines (Ramos, Raji, and SUDHL4; see also Supplementary Figure 2). Data in (C–E) are representative of three independent experiments with distinct cell aliquots or tonsil specimens. Ctrl, vector control; ST3OE, ST3Gal1OE.