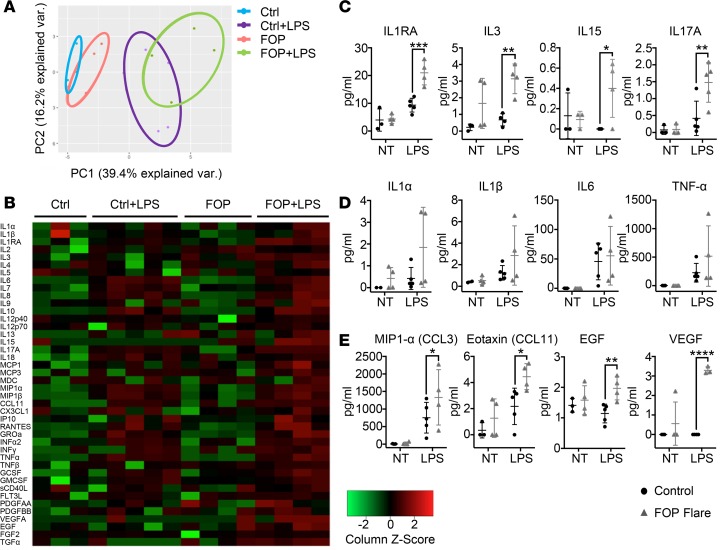
Figure 5. LPS-stimulated FOP monocytes show abnormal proinflammatory cytokine secretion.
Supernatants were collected from monocytes of control (n ≥ 3) and FOP (n = 4) subjects. Monocytes untreated (NT) and LPS-stimulated (10 ng/ml) for 24 hours were assayed for 41 cytokines. (A) Shapes represent expression profiles of the different donors in principle component analysis (PCA). (B) Heatmap representing color-coded cytokine secretion by Control, Control+LPS, FOP, FOP+LPS samples. (C) Proinflammatory cytokines IL-1RA, IL-3, IL-15, and IL-17A were significantly increased in FOP LPS-stimulated monocytes. (D) Typical proinflammatory cytokines IL-1α/β, IL-6, and TNF-α production were increased upon LPS stimulation but not significantly different among control and FOP subjects. (E) Chemokine ligands CCL3 and CCL11 and growth factors EGF and VEGF were significantly increased in FOP monocytes stimulated with LPS. The distribution of the subjects is described in Supplemental Table 6. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 by Sidak’s multiple comparison test. Error bars represent means ± 1 SD.