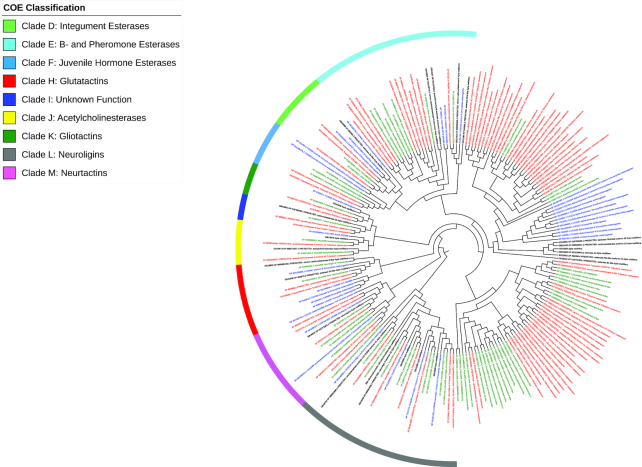
Figure 9:
Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree of carboxylesterase (COE) genes. The maximum likelihood bootstrap consensus tree (1,000 replicates) showing the relationships among COE genes from the genomes of A. tumida (ATUMI) in green, A. mellifera (AMELL) in black, D. melanogaster (DMELA) in blue, and T. castaneum (TCAST) in red, identified manually using the Uniprot and Pfam databases. Branches corresponding to partitions recovered in less than 50% of bootstrap replicates are collapsed. Starting tree(s) for the heuristic search was obtained automatically using neighbor-joining and BioNJ algorithms applied to a matrix of pairwise distances estimated using a JTT model and then selecting the topology with the superior log likelihood value. All positions with less than 95% site coverage were eliminated. The phylogenetically distinct clusters were named according to established nomenclature for COE genes [12]. The tree was annotated and visualized with the iToL web tool [24].